3D Laser Cutting: A Revolutionary Technology for Precision Manufacturing
Introduction
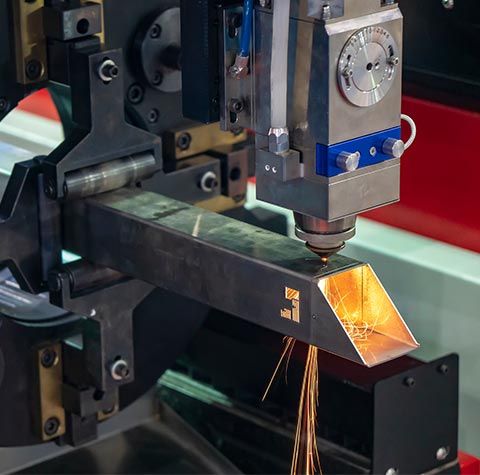
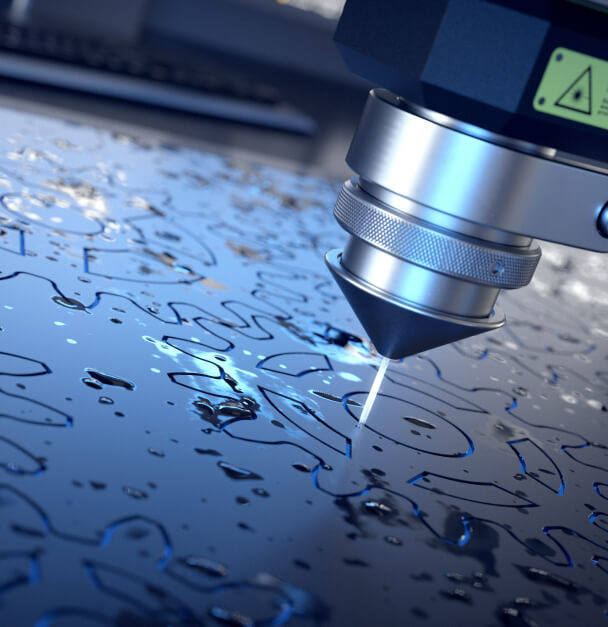
3D laser cutting, a transformative technology in the manufacturing industry, has revolutionized the way complex and intricate parts are produced. It employs a focused laser beam to cut through various materials with unmatched precision and efficiency. This article delves into the world of 3D laser cutting, exploring its principles, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Laser Cutting: A Revolutionary Technology for Precision Manufacturing
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 How 3D Laser Cutting Works
- 1.3 Types of 3D Laser Cutting Systems
- 1.4 Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.5 How 3D Laser Cutting Works
- 1.6 Types of 3D Laser Cutting Systems
- 1.7 Benefits of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.8 Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.9 Future Prospects of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.10 Conclusion
- 1.11 FAQs
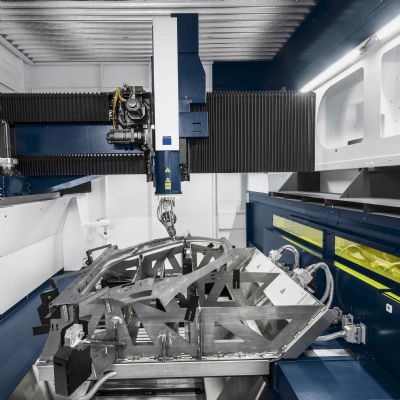
How 3D Laser Cutting Works
Types of 3D Laser Cutting Systems
There are two primary types of 3D laser cutting systems:
1. Gantry-Based Systems: These systems feature a laser head mounted on a gantry that moves along the X and Y axes. The material is positioned on a table that moves along the Z axis.
2. Robotic Arm Systems: These systems utilize a robotic arm to manipulate the laser head, providing greater flexibility and the ability to cut complex geometries.
Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting is versatile and can be used with a wide range of materials, including:
- Metals: Steel, aluminum, stainless steel, titanium
- Plastics: Acrylic, polycarbonate, polyethylene
- Wood: Plywood, MDF, hardwoods
- Shapeways Laser Cutting Shapeways Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Advanced Manufacturing
- Laser Cutter Comparable To Glowforge Laser Cutter Comparable To Glowforge: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut 3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Precision Fabrication
- Thingiverse Laser Cut Thingiverse Laser Cut: Unleashing The Power Of Digital Fabrication
- Paper and Cardboard: Corrugated board, honeycomb board
- Composites: Carbon fiber, fiberglass
3D laser cutting, a transformative technology in the manufacturing industry, has revolutionized the way complex and intricate parts are produced. It employs a focused laser beam to cut through various materials with unmatched precision and efficiency. This article delves into the world of 3D laser cutting, exploring its principles, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
How 3D Laser Cutting Works
The 3D laser cutting process involves directing a high-powered laser beam onto the surface of the target material. The laser energy melts, vaporizes, or burns the material, creating a precise cut. The laser beam is guided by a computer-aided design (CAD) file, which defines the desired cut path.
Types of 3D Laser Cutting Systems
There are two primary types of 3D laser cutting systems:
1. Gantry-Based Systems: These systems feature a laser head mounted on a gantry that moves along the X and Y axes. The material is positioned on a table that moves along the Z axis.
Benefits of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting offers numerous advantages over traditional cutting methods:
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser beams provide extremely precise cuts with tight tolerances and smooth edges.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting is significantly faster than manual or mechanical cutting, reducing production time.
- Versatility: 3D laser cutting can handle a wide range of materials and geometries, making it suitable for diverse applications.
- Reduced Waste: Laser cutting minimizes material waste by creating precise cuts and eliminating the need for secondary finishing operations.
- Automation and Repeatability: CAD files enable automated cutting processes, ensuring consistent results and repeatability.
Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting has found widespread applications in various industries, including:
- Automotive: Cutting of body panels, exhaust systems, and other components
- Aerospace: Fabrication of aircraft parts, engine components, and structural elements
- Medical: Production of surgical instruments, prosthetics, and medical devices
- Consumer Electronics: Cutting of smartphone cases, tablet enclosures, and other electronic components
- Architecture: Creation of decorative panels, architectural models, and custom lighting fixtures
Future Prospects of 3D Laser Cutting
The future of 3D laser cutting holds immense potential for further advancements and applications. Key areas of development include:
- Multi-Axis Cutting: Systems with additional axes of motion will enable even more complex and intricate cuts.
- Ultrafast Lasers: Lasers with shorter pulse durations will increase cutting speeds and reduce heat-affected zones.
- Additive Manufacturing Integration: 3D laser cutting can be combined with additive manufacturing to create hybrid processes for producing complex parts.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms will enhance system automation, optimize cutting parameters, and improve quality control.
Conclusion
3D laser cutting is a groundbreaking technology that has transformed the manufacturing industry. Its precision, speed, and versatility make it an ideal solution for creating complex and intricate parts in a wide range of materials. As the technology continues to evolve, it holds immense potential for further advancements and applications, unlocking new possibilities for innovation and productivity.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between 3D laser cutting and 2D laser cutting?
A1: 3D laser cutting involves cutting along the X, Y, and Z axes, allowing for the creation of three-dimensional shapes. 2D laser cutting, on the other hand, cuts only along the X and Y axes.
Q2: How thick can 3D laser cutting cut?
A2: The maximum cutting thickness depends on the laser power and material being cut. Typically, 3D laser cutting can cut through materials up to several inches thick.
Q3: What is the best material for 3D laser cutting?
A3: The optimal material depends on the specific application. Metals like steel and aluminum are suitable for high-strength components, while plastics and wood are ideal for lightweight or decorative parts.
Q4: Is 3D laser cutting expensive?
A4: The cost of 3D laser cutting varies depending on factors such as the size, complexity, and material of the part. However, it can be a cost-effective solution for high-volume production or complex geometries.
Q5: What are the safety considerations for 3D laser cutting?
A5: Laser cutting generates intense light and fumes. Proper safety measures, including protective eyewear, ventilation systems, and enclosed cutting areas, are essential to ensure operator safety.



















