3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to Precision Fabrication
Introduction
3D laser cutting has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, enabling the creation of intricate and complex parts with unparalleled precision. This cutting-edge technology utilizes a focused laser beam to melt, vaporize, or burn materials, resulting in precise cuts along three-dimensional surfaces. This article provides an in-depth exploration of 3D laser cutting, covering its principles, applications, benefits, and considerations.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to Precision Fabrication
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 How Does 3D Laser Cutting Work?
- 1.3 Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.4 How Does 3D Laser Cutting Work?
- 1.5 Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.6 Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.7 Benefits of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.8 Considerations for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.9 Conclusion
- 1.10 FAQs
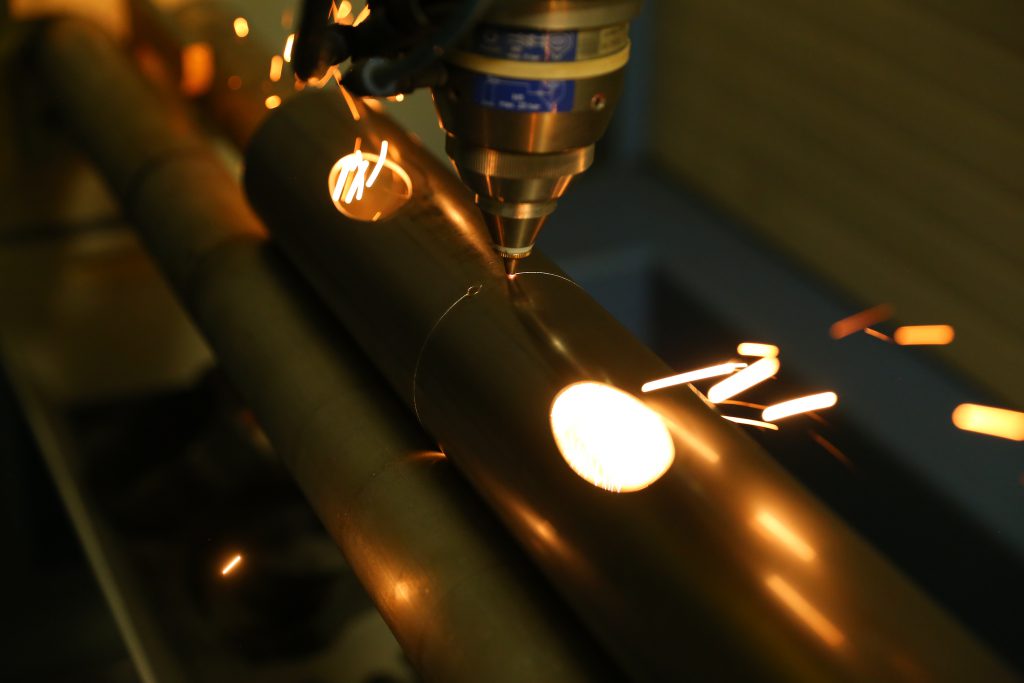
How Does 3D Laser Cutting Work?
The laser cutting process is controlled by a computer numerical control (CNC) system, which follows a pre-programmed toolpath to guide the laser beam precisely. The CNC system ensures that the laser beam follows the desired cutting path, resulting in accurate and repeatable cuts.
Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting is compatible with a wide range of materials, including:
- Metals (e.g., steel, aluminum, stainless steel)
- Plastics (e.g., acrylic, polycarbonate, polyethylene)
- Wood
- Ceramics
- Glass
3D laser cutting has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, enabling the creation of intricate and complex parts with unparalleled precision. This cutting-edge technology utilizes a focused laser beam to melt, vaporize, or burn materials, resulting in precise cuts along three-dimensional surfaces. This article provides an in-depth exploration of 3D laser cutting, covering its principles, applications, benefits, and considerations.
How Does 3D Laser Cutting Work?
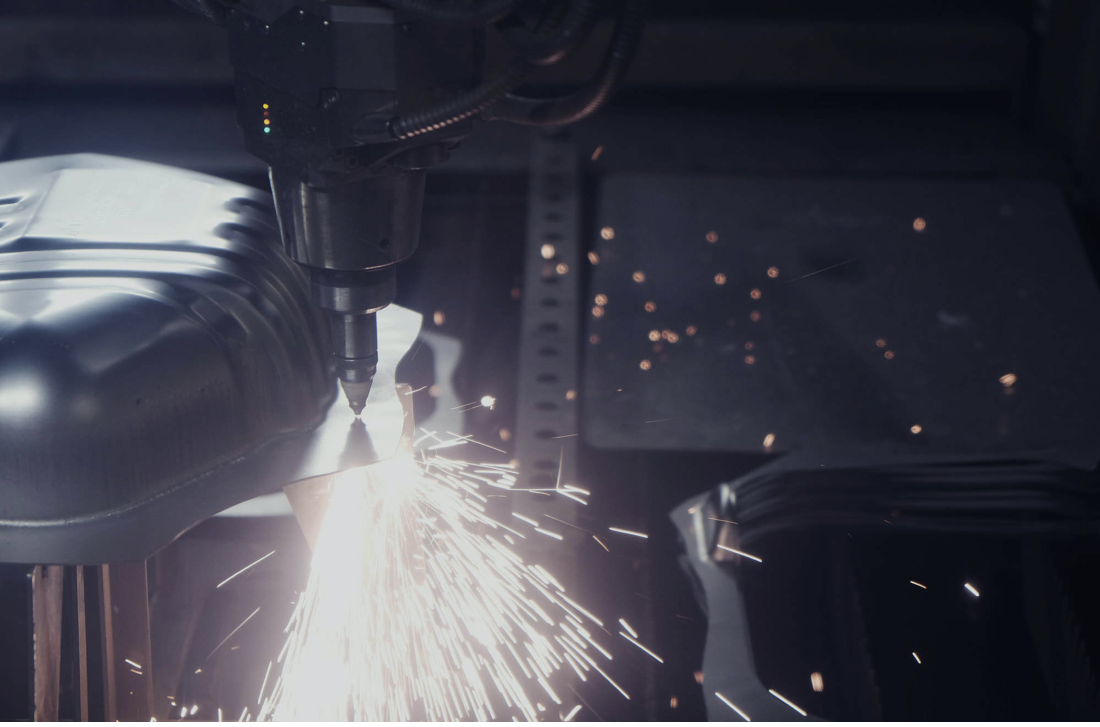
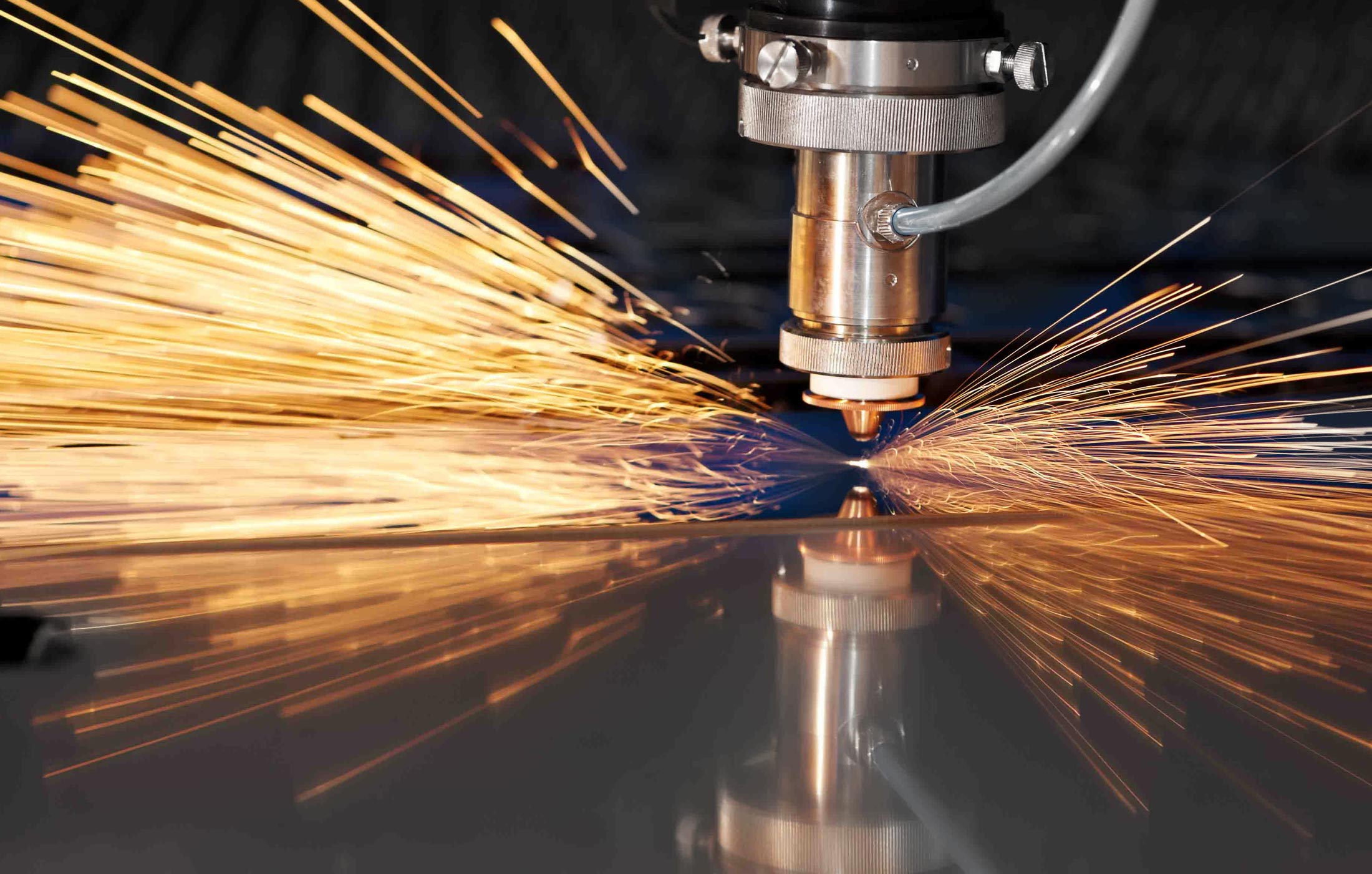
3D laser cutting employs a computerized system that directs a laser beam along predefined paths on a workpiece. The laser beam is typically generated by a fiber laser or a CO2 laser, which emits a high-energy, concentrated beam of light. As the laser beam interacts with the material, it transfers thermal energy, causing the material to melt, vaporize, or burn.
The laser cutting process is controlled by a computer numerical control (CNC) system, which follows a pre-programmed toolpath to guide the laser beam precisely. The CNC system ensures that the laser beam follows the desired cutting path, resulting in accurate and repeatable cuts.
Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting is compatible with a wide range of materials, including:
The choice of material depends on the specific application and the desired properties of the finished product.
Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting finds applications in a vast array of industries, including:
- Aerospace: Fabrication of complex aircraft components, such as engine parts and wing structures
- Automotive: Production of intricate body panels, interior components, and exhaust systems
- Medical: Creation of surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics
- Electronics: Manufacturing of circuit boards, electronic enclosures, and connectors
- Art and Design: Production of sculptures, jewelry, and decorative pieces

Benefits of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting offers numerous advantages over traditional cutting methods:
- High Precision: Laser cutting provides exceptional accuracy, with cutting tolerances as low as ±0.001 inches.
- Complex Geometries: 3D laser cutting enables the creation of complex and intricate shapes that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting is a fast and efficient process, reducing production time and increasing productivity.
- Reduced Waste: Laser cutting minimizes material waste by following precise cutting paths, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Automation: The CNC system allows for automated operation, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing human error.

Considerations for 3D Laser Cutting
When considering 3D laser cutting for a specific application, several factors should be taken into account:
- Material Properties: The suitability of the material for laser cutting depends on its melting point, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity.
- Cut Quality: The desired cut quality, including surface finish, edge sharpness, and accuracy, must be considered.
- Machine Capabilities: The size, power, and capabilities of the laser cutting machine must match the requirements of the application.
- Cost: The cost of laser cutting depends on factors such as material, complexity of the design, and production volume.
Conclusion
3D laser cutting is a transformative technology that has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. Its ability to create precise and complex parts with high speed and efficiency makes it an invaluable tool for a wide range of applications. By understanding the principles, applications, benefits, and considerations of 3D laser cutting, manufacturers can leverage this technology to enhance their production capabilities and achieve competitive advantages.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between 2D and 3D laser cutting?
A: 2D laser cutting operates on a flat surface, while 3D laser cutting can cut along three-dimensional surfaces, creating complex shapes.
Q: What are the safety precautions for 3D laser cutting?
A: Proper ventilation, eye protection, and protective clothing are essential to ensure safety during laser cutting operations.
Q: How does the laser power affect the cut quality?
A: Higher laser power results in faster cutting speeds and cleaner cuts, but it can also lead to heat-affected zones if not controlled properly.
Q: What is the typical lifespan of a laser cutting machine?
A: The lifespan of a laser cutting machine depends on factors such as maintenance, usage, and environmental conditions, but it typically ranges from 10 to 20 years.
Q: Can 3D laser cutting be used for mass production?
A: Yes, 3D laser cutting can be automated for mass production, offering high speed and consistency.