3D Laser Printing: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Design
Introduction
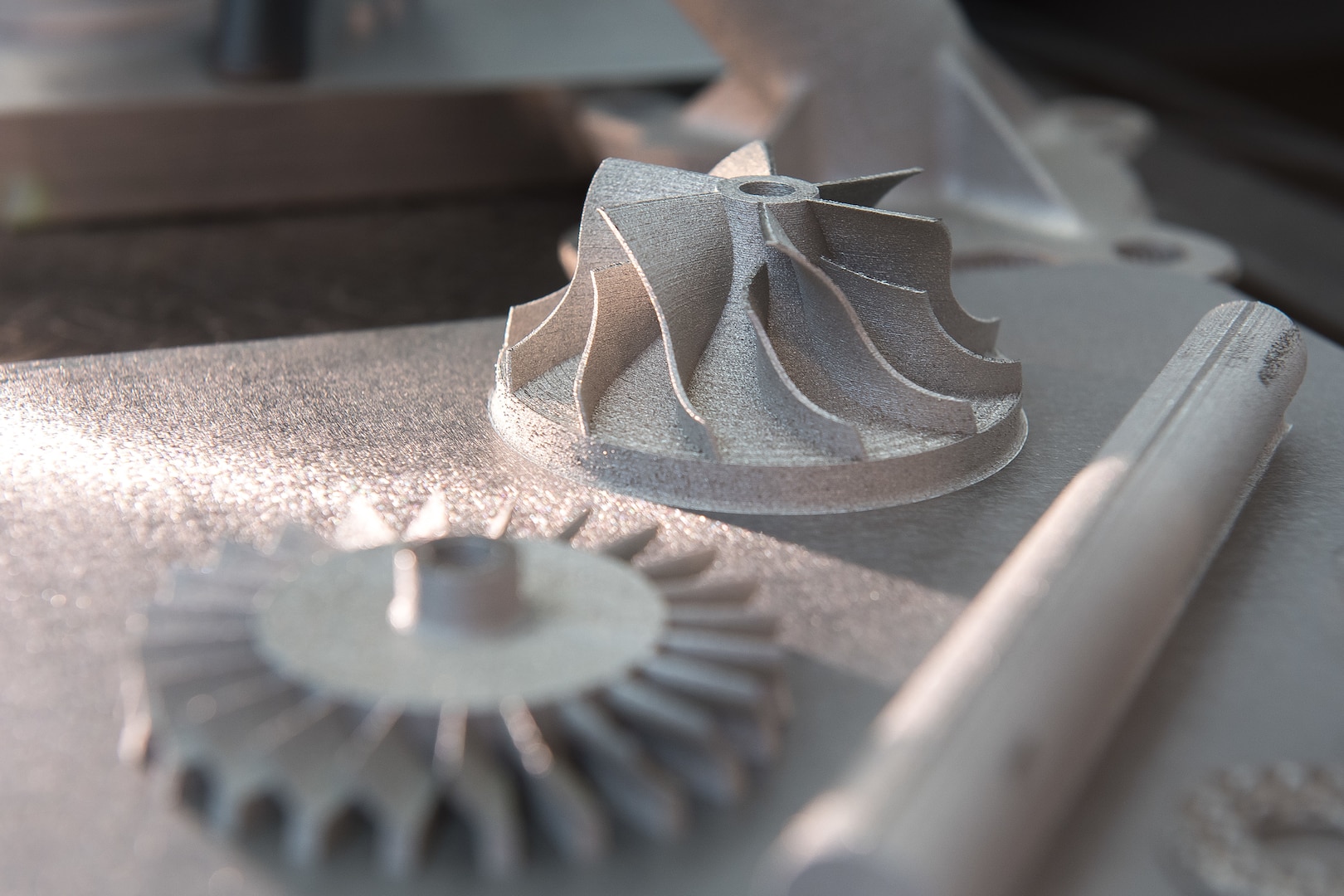
3D laser printing, also known as laser sintering or selective laser melting (SLM), is an advanced manufacturing technology that enables the creation of complex three-dimensional objects directly from digital design files. It utilizes a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials, layer by layer, to build intricate shapes and structures.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Laser Printing: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Design
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 How 3D Laser Printing Works
- 1.3 Advantages of 3D Laser Printing
- 1.4 How 3D Laser Printing Works
- 1.5 Applications of 3D Laser Printing
- 1.6 Materials Used in 3D Laser Printing
- 1.7 Factors Affecting 3D Laser Printing Quality
- 1.8 Conclusion
- 1.9 FAQs
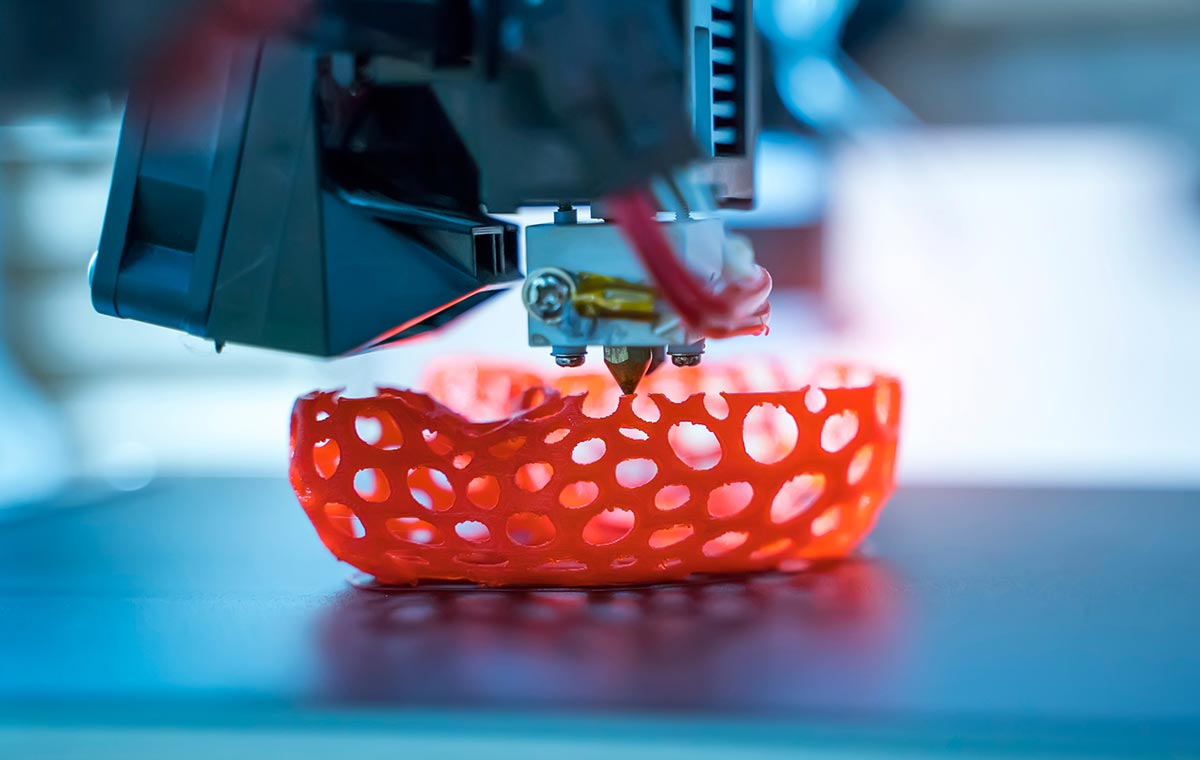
How 3D Laser Printing Works
- CAD Modeling: A 3D model of the desired object is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- File Slicing: The CAD model is sliced into thin layers, representing the cross-sections of the object.
- Laser Fusion: A high-powered laser is used to scan and selectively fuse the powdered material, following the sliced layers.
- Layer Deposition: The laser fuses the material, creating a solid layer that bonds to the previous layer.
- Part Creation: The process is repeated layer by layer until the entire object is built.
Advantages of 3D Laser Printing
3D laser printing offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
- Laser Cutting 3d Printer Laser Cutting 3D Printer: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Cutting Machine 3D Cutting Machine: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cutting Wood 3D Laser Cutting Wood: A Comprehensive Guide
- Laser Cut 3d Animal Puzzle Laser Cut 3D Animal Puzzle: A Journey Into Intricate Wooden Masterpieces
- Laser Cut 3d Holiday Cards Laser Cut 3D Holiday Cards: A Festive And Unique Way To Spread Cheer
- CAD Modeling: A 3D model of the desired object is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- File Slicing: The CAD model is sliced into thin layers, representing the cross-sections of the object.
- Rapid Prototyping: Allows for quick and cost-effective creation of prototypes and design iterations.
- Complex Geometries: Enables the production of intricate shapes and structures that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
- Customization: Supports the creation of customized and personalized products.
- Reduced Waste: Minimizes material waste by only using the material required for the object’s construction.
- Increased Efficiency: Automates the manufacturing process, reducing labor costs and increasing production efficiency.
3D laser printing, also known as laser sintering or selective laser melting (SLM), is an advanced manufacturing technology that enables the creation of complex three-dimensional objects directly from digital design files. It utilizes a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials, layer by layer, to build intricate shapes and structures.
How 3D Laser Printing Works
The 3D laser printing process involves several steps:
Applications of 3D Laser Printing
3D laser printing finds applications in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: Production of complex aircraft components, satellite parts, and rocket engines.
- Automotive: Design and prototyping of automotive parts, such as engine components and interior trim.
- Medical: Creation of surgical implants, medical devices, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
- Consumer Products: Manufacturing of electronic devices, toys, and home goods.
- Industrial: Production of tooling, molds, and custom parts.
Materials Used in 3D Laser Printing
Various materials can be used in 3D laser printing, including:
- Metals: Stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and cobalt-chromium alloys.
- Plastics: Nylon, ABS, polycarbonate, and PEEK.
- Composites: Mixtures of materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers.
- Ceramics: Alumina, zirconia, and hydroxyapatite.
Factors Affecting 3D Laser Printing Quality
The quality of 3D laser-printed parts is influenced by several factors:
- Laser Power: The power of the laser used to fuse the material.
- Material Properties: The melting point, density, and flowability of the material.
- Layer Thickness: The thickness of the layers deposited during the printing process.
- Scan Speed: The speed at which the laser scans the material.
- Post-Processing: Additional steps, such as heat treatment or surface finishing, to improve part properties.
Conclusion
3D laser printing is a transformative technology that has revolutionized manufacturing and design. It enables the creation of complex and intricate objects with high precision and efficiency. As the technology continues to evolve, it is expected to have an even greater impact on industries worldwide.
FAQs
Q: What are the limitations of 3D laser printing?
A: Current limitations include the size of objects that can be printed, the cost of high-end materials, and the need for post-processing in some cases.
Q: How does 3D laser printing compare to other 3D printing technologies?
A: 3D laser printing is generally more precise and produces stronger parts than other 3D printing methods, but it can be more expensive.
Q: What is the future of 3D laser printing?
A: The future of 3D laser printing is promising, with advancements in materials, software, and hardware expected to drive further innovation and applications.