3D Laser Scanning: A Comprehensive Guide to Revolutionary Measurement Technology
Introduction
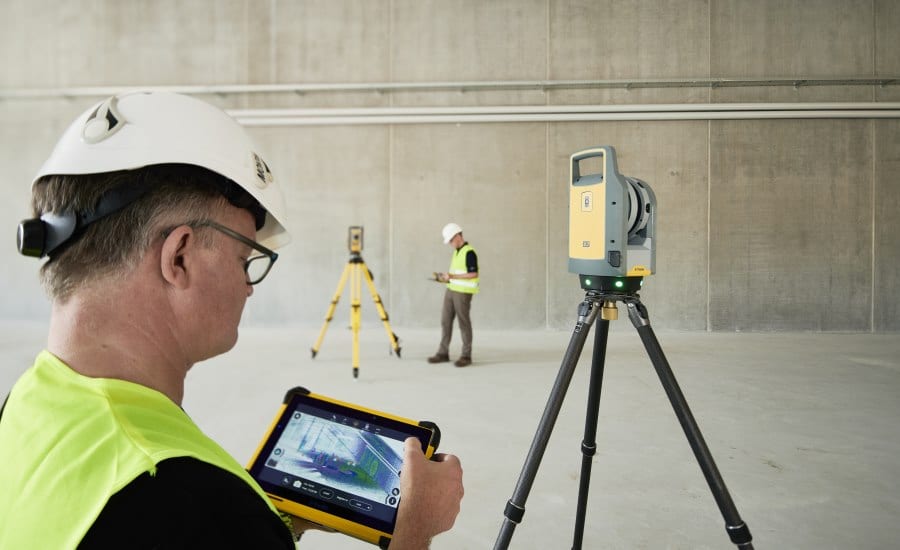
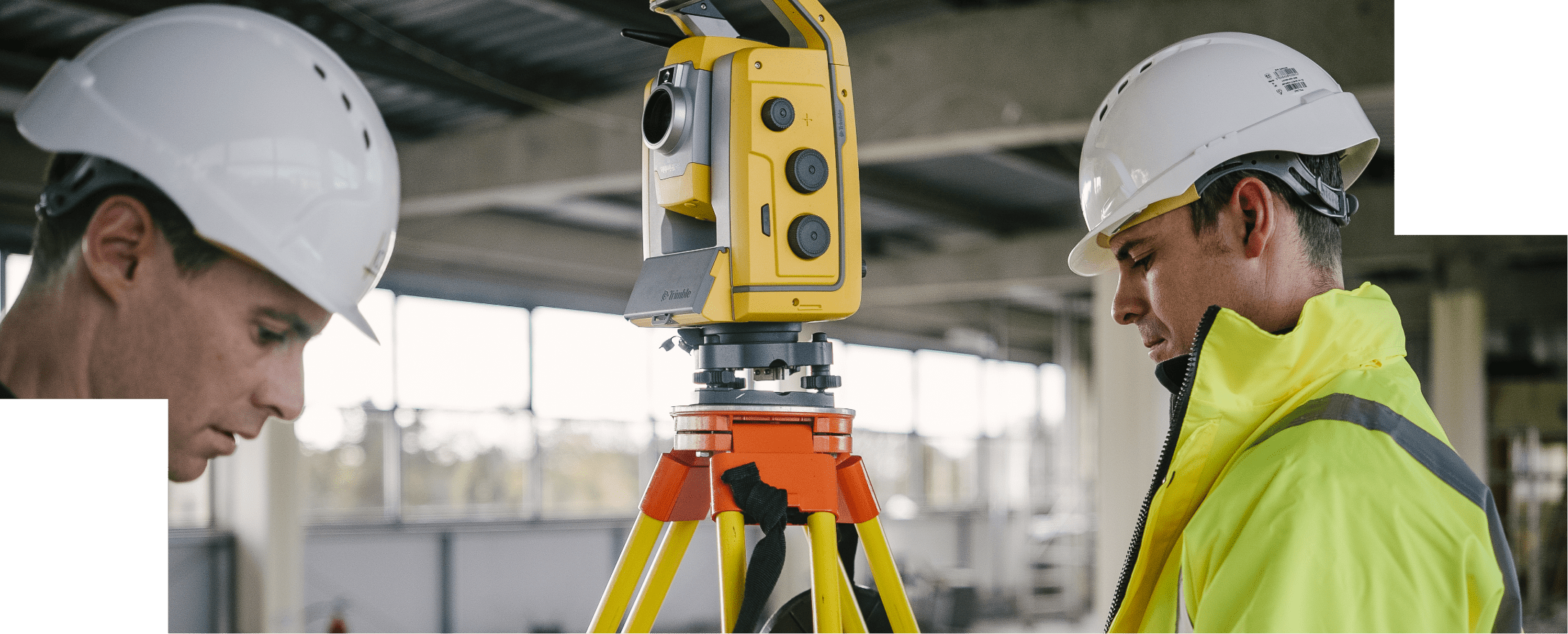
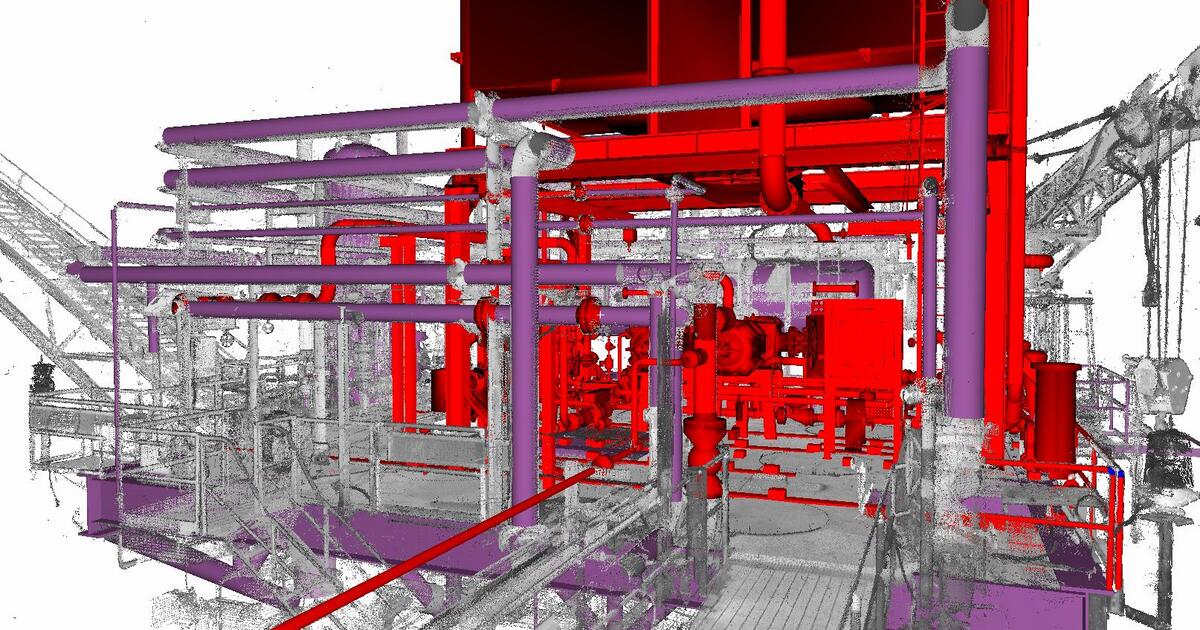
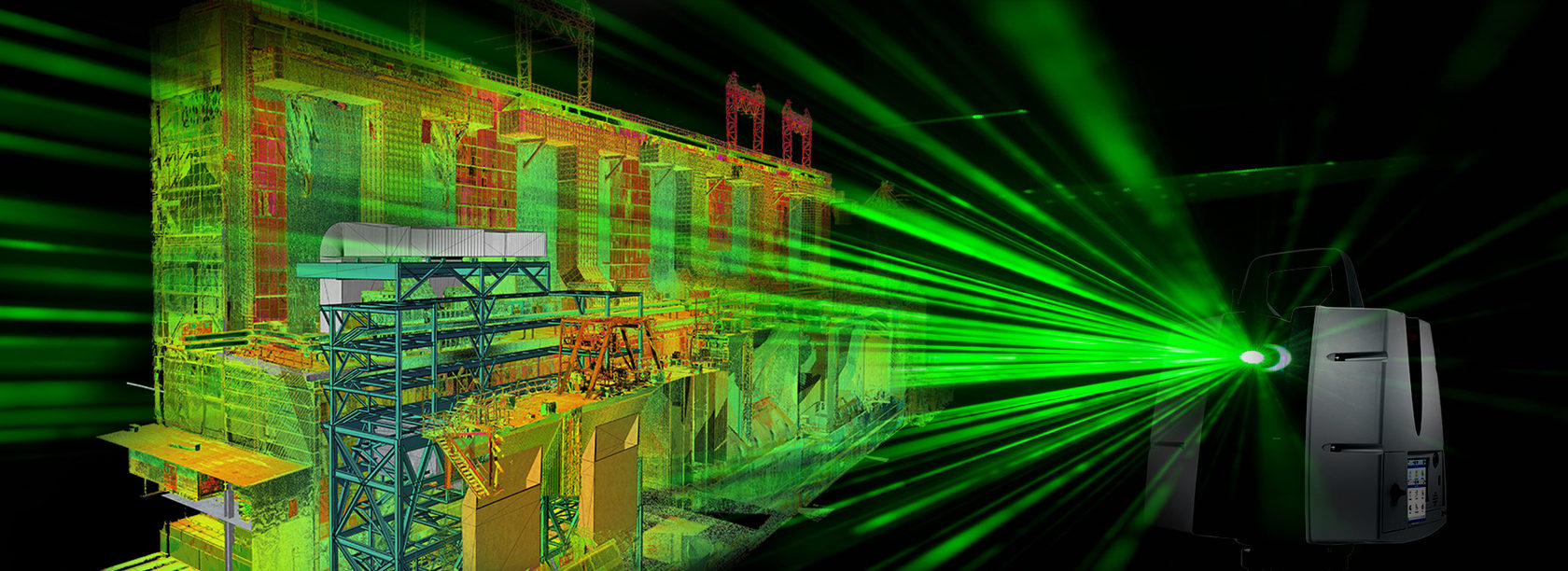
3D laser scanning, also known as lidar (light detection and ranging), is a non-contact measurement technology that utilizes lasers to capture highly accurate and detailed three-dimensional representations of objects and environments. This innovative technique has revolutionized various industries, including construction, engineering, architecture, and manufacturing, by providing precise and comprehensive data for design, planning, and inspection purposes.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Laser Scanning: A Comprehensive Guide to Revolutionary Measurement Technology
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?
- 1.3 Types of 3D Laser Scanners
- 1.4 Applications of 3D Laser Scanning
- 1.5 How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?
- 1.6 Types of 3D Laser Scanners
- 1.7 Benefits of 3D Laser Scanning
- 1.8 Challenges of 3D Laser Scanning
- 1.9 Conclusion
- 1.10 FAQs
How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?
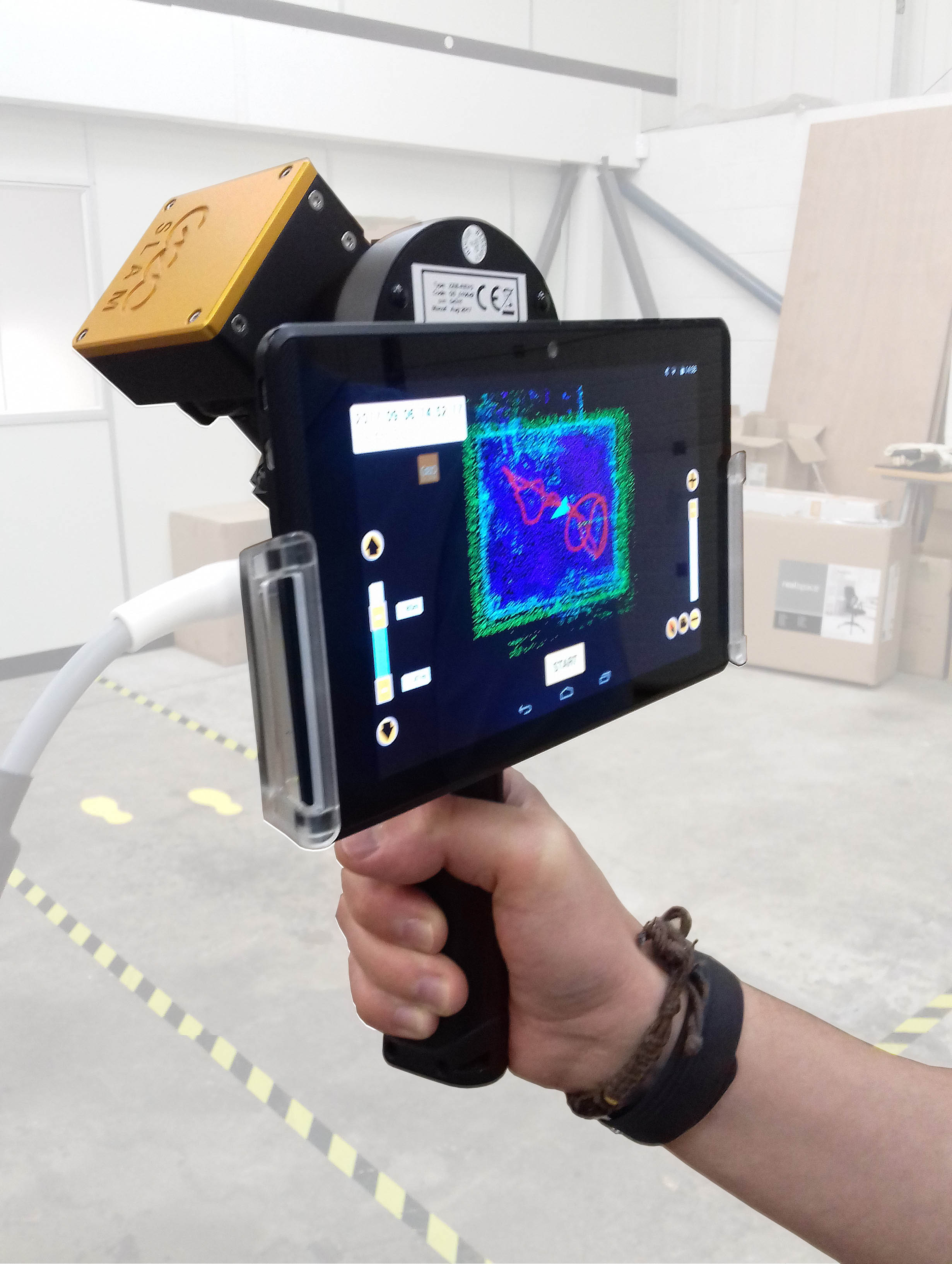
By rotating and moving the scanner around the object, the laser beam can capture millions of data points, creating a dense point cloud that represents the object’s shape and geometry. This point cloud can then be processed to generate high-resolution 3D models, orthographic views, and other valuable data.
Types of 3D Laser Scanners
There are two primary types of 3D laser scanners:
- Time-of-Flight (TOF) Scanners: These scanners measure the time it takes for the laser beam to travel to and from the object’s surface. They are typically used for long-range scanning applications, such as surveying and mapping.
- Phase-Shift Scanners: These scanners measure the phase shift of the laser beam as it reflects off the object’s surface. They are typically used for short-range scanning applications, such as object inspection and reverse engineering.
Applications of 3D Laser Scanning
3D laser scanning has numerous applications across a wide range of industries:
Construction:
3D laser scanning, also known as lidar (light detection and ranging), is a non-contact measurement technology that utilizes lasers to capture highly accurate and detailed three-dimensional representations of objects and environments. This innovative technique has revolutionized various industries, including construction, engineering, architecture, and manufacturing, by providing precise and comprehensive data for design, planning, and inspection purposes.
- 3d And Laser Cut 3D And Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
- 3d Laser Cut Bee 3D Laser Cut Bee: A Buzzing Masterpiece Of Precision And Creativity
- 3d Laser Cut Metal Models 3D Laser Cut Metal Models: A Comprehensive Guide To Precision And Creativity
- 3d Laser Cut Templates Free 3D Laser Cut Templates Free: Unleash Your Creativity With Precision
- Laser Cut 3d Dragon Laser Cut 3D Dragon: A Detailed Guide To Crafting A Majestic Masterpiece
How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?
A 3D laser scanner emits a pulsed laser beam that interacts with the surface of the object being scanned. The beam reflects off the surface, and the scanner measures the time it takes for the beam to return to the scanner. This time measurement, combined with the known speed of light, allows the scanner to calculate the distance between the scanner and the object’s surface.
By rotating and moving the scanner around the object, the laser beam can capture millions of data points, creating a dense point cloud that represents the object’s shape and geometry. This point cloud can then be processed to generate high-resolution 3D models, orthographic views, and other valuable data.
Types of 3D Laser Scanners
There are two primary types of 3D laser scanners:
- As-built documentation
- BIM (Building Information Modeling)
- Construction progress monitoring
- Quality control and inspection
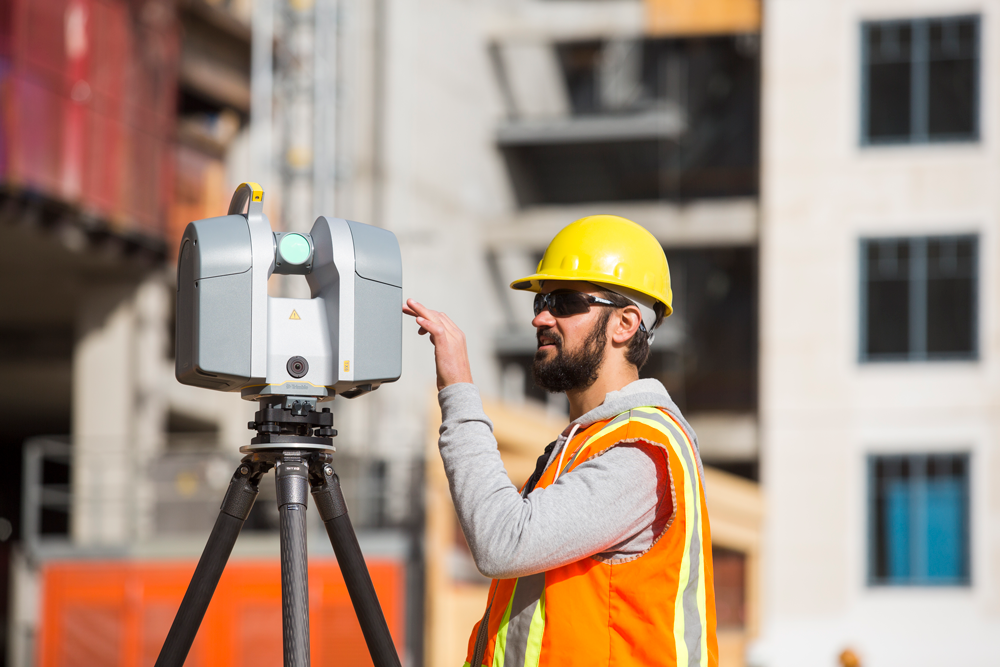

Engineering:
- Reverse engineering
- Product design and development
- Inspection and maintenance
- Deformation and vibration analysis
Architecture:
- Heritage documentation
- Architectural design and modeling
- Space planning and interior design
- Facility management
Manufacturing:
- Inspection and quality control
- Reverse engineering and product development
- Assembly line optimization
- Robot guidance and automation
Benefits of 3D Laser Scanning
3D laser scanning offers several advantages over traditional measurement methods:
- Accuracy and Precision: Laser scanners capture highly accurate and precise data, enabling the creation of highly detailed 3D models.
- Non-Contact Measurement: Laser scanning does not require physical contact with the object being scanned, making it ideal for delicate or inaccessible objects.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser scanners can capture large amounts of data quickly and efficiently, reducing the time required for data collection.
- Comprehensive Data: Laser scanners capture not only the shape and geometry of objects but also their texture and color information, providing a rich and complete dataset.
- Versatility: Laser scanning can be used in a wide range of applications, from small-scale object inspection to large-scale surveying and mapping projects.
Challenges of 3D Laser Scanning
Despite its numerous benefits, 3D laser scanning also has some challenges:
- Data Processing: The large volume of data captured by laser scanners requires powerful computers and specialized software for processing and analysis.
- Environmental Conditions: Laser scanning can be affected by environmental factors such as dust, fog, and direct sunlight, which can reduce the accuracy and completeness of the data.
- Cost: High-quality 3D laser scanners can be expensive, especially for large-scale projects.
- Operator Skill: Skilled operators are required to operate laser scanners and interpret the data accurately.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning is a revolutionary measurement technology that has transformed various industries by providing highly accurate and detailed 3D data. Its versatility, speed, and non-contact nature make it an indispensable tool for design, planning, inspection, and other applications. While there are some challenges associated with 3D laser scanning, such as data processing and environmental conditions, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a 3D laser scanner and a traditional surveying instrument?
A: 3D laser scanners capture dense point clouds that represent the shape and geometry of objects, while traditional surveying instruments measure specific points and angles. Laser scanners provide a more comprehensive and detailed dataset.
Q: How long does it take to scan an object using a 3D laser scanner?
A: The scanning time varies depending on the size and complexity of the object, as well as the resolution and accuracy settings of the scanner. Small objects can be scanned in a few minutes, while large objects or environments may take several hours or even days.
Q: What software is used to process 3D laser scan data?
A: There are various software packages available for processing 3D laser scan data. Some popular options include Autodesk Recap, Bentley ContextCapture, and Trimble RealWorks.
Q: What are the key considerations when choosing a 3D laser scanner?
A: When selecting a 3D laser scanner, consider the following factors: accuracy and precision, range and resolution, scanning speed, environmental conditions, and cost.