3D Printers and Laser Cutters: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
3D printers and laser cutters are two cutting-edge technologies that have revolutionized the manufacturing industry. They offer a wide range of capabilities, enabling the creation of complex and precise objects from a variety of materials. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of 3D printers and laser cutters, exploring their functionalities, applications, and key differences.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Printers and Laser Cutters: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 1. 3D Printers: Building Objects from Scratch
- 2.1 H2.2 Materials Used in 3D Printing
- 3 1. 3D Printers: Building Objects from Scratch
- 3.2 H2.1 How 3D Printers Work
- 3.3 H2.3 Applications of 3D Printing
- 4 2. Laser Cutters: Precision Cutting and Engraving
- 4.4 H2.1 How Laser Cutters Work
- 4.5 H2.2 Materials Cut and Engraved by Laser Cutters
- 4.6 H2.3 Applications of Laser Cutting
- 5 3. Key Differences Between 3D Printers and Laser Cutters
- 5.7 H3.1 Functionality
- 5.8 H3.2 Materials Used
- 5.9 H3.3 Applications
- 6 4. Choosing Between 3D Printers and Laser Cutters
- 7 5. Conclusion
- 8 FAQs
- 8.10 Q1. What is the difference between 3D modeling and 3D printing?
- 8.11 Q2. Can 3D printers be used for metalworking?
- 8.12 Q3. What is the advantage of using a laser cutter over a traditional saw?
- 8.13 Q4. Are 3D printers or laser cutters more expensive?
- 8.14 Q5. What are some safety precautions to follow when using 3D printers and laser cutters?
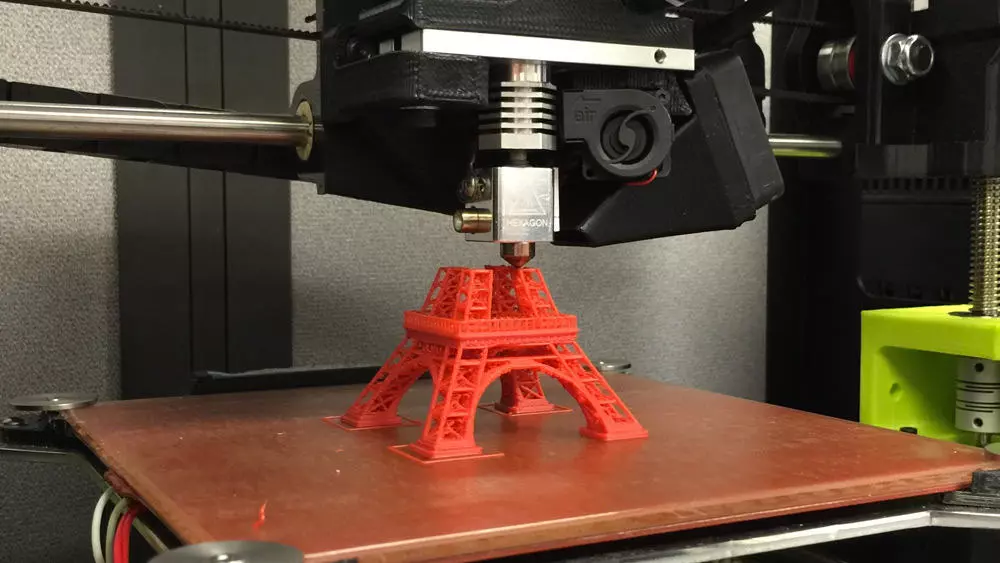
1. 3D Printers: Building Objects from Scratch
3D printers operate on the principle of additive manufacturing, where objects are constructed layer by layer. They take digital 3D models as input and convert them into physical objects by depositing material in precise locations. The most common types of 3D printers include:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Melts and extrudes thermoplastic filament to create objects.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Uses a laser to cure liquid resin, building objects from the bottom up.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Bonds powdered material using a laser, creating durable and complex objects.
H2.2 Materials Used in 3D Printing
3D printers can utilize a variety of materials, including:
- Thermoplastics (PLA, ABS, PETG): Common materials for FDM printing, offering flexibility and durability.
- Thingiverse Laser Cut Thingiverse Laser Cut: Unleashing The Power Of Digital Fabrication
- 3d Laser Cut 3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Precision Fabrication
- 3d Laser Wood Cutter 3D Laser Wood Cutter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Laser Cutter Comparable To Glowforge Laser Cutter Comparable To Glowforge: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut Wood 3D Laser Cut Wood: Unlocking Intricate Designs And Precision Craftsmanship
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Melts and extrudes thermoplastic filament to create objects.
- Photopolymers (resins): Used in SLA printing, known for their high resolution and smooth surfaces.
- Metal powders (titanium, stainless steel): Enable the creation of strong and lightweight metal parts using SLS.
- Prototyping: Creating physical models for design validation and testing.
- Manufacturing: Producing custom parts, tools, and end-use products.
- Healthcare: Fabricating medical implants, prosthetics, and surgical guides.
- Art and Design: Creating sculptures, jewelry, and decorative objects.
- CO2 Laser Cutters: Use carbon dioxide gas to generate the laser beam, capable of cutting a wide range of materials.
- Fiber Laser Cutters: Utilize a fiber-optic cable to deliver the laser beam, offering high cutting speeds and precision.
- Wood: Commonly used for cutting and engraving, offering versatility and natural aesthetics.
- Acrylic: A durable and transparent material suitable for laser cutting and engraving.
- Metal: Laser cutters can cut thin sheets of metal, such as stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Fabric: Laser cutters can engrave and cut fabrics, such as leather, denim, and cotton.
- Fabrication: Creating custom parts, signs, and decorative elements.
- Prototyping: Producing prototypes and models for testing and evaluation.
- Art and Design: Engraving and cutting designs on wood, acrylic, and other materials for artistic purposes.
- Textile Industry: Cutting and engraving fabrics for clothing, upholstery, and accessories.
- 3D printers build objects from scratch by adding material layer by layer.
- Laser cutters cut or engrave materials using a focused laser beam.
- 3D printers use a wide range of materials, including thermoplastics, photopolymers, and metal powders.
- Laser cutters handle materials such as wood, acrylic, metal, and fabric.
- 3D printers excel in prototyping, manufacturing, healthcare, and art.
- Laser cutters are ideal for fabrication, prototyping, art, and the textile industry.
- Object Complexity: 3D printers can create complex 3D objects, while laser cutters are better suited for 2D designs and cutting.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure that the desired material is compatible with the chosen technology.
- Accuracy and Precision: Laser cutters offer higher precision and detail compared to most 3D printers.
- Cost and Maintenance: Both 3D printers and laser cutters can vary in price and maintenance requirements.

3D printers and laser cutters are two cutting-edge technologies that have revolutionized the manufacturing industry. They offer a wide range of capabilities, enabling the creation of complex and precise objects from a variety of materials. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of 3D printers and laser cutters, exploring their functionalities, applications, and key differences.
1. 3D Printers: Building Objects from Scratch
H2.1 How 3D Printers Work
3D printers operate on the principle of additive manufacturing, where objects are constructed layer by layer. They take digital 3D models as input and convert them into physical objects by depositing material in precise locations. The most common types of 3D printers include:
H2.3 Applications of 3D Printing
3D printers are versatile tools with applications in various industries, such as:

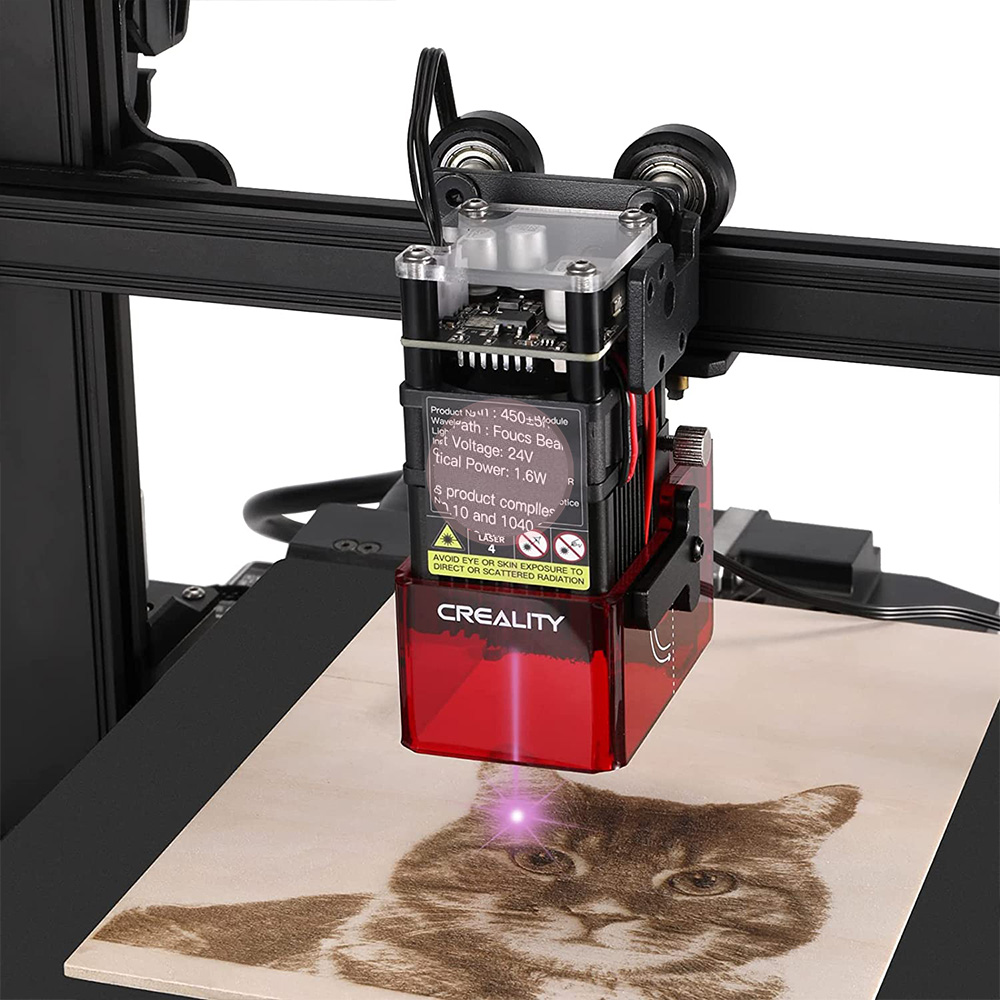
2. Laser Cutters: Precision Cutting and Engraving
H2.1 How Laser Cutters Work
Laser cutters use a focused beam of laser light to cut or engrave materials. The laser beam is directed by a computer-controlled system, allowing for precise and intricate designs. The most common types of laser cutters include:
H2.2 Materials Cut and Engraved by Laser Cutters
Laser cutters can handle a variety of materials, including:
H2.3 Applications of Laser Cutting
Laser cutters find applications in numerous industries, such as:
3. Key Differences Between 3D Printers and Laser Cutters
H3.1 Functionality
H3.2 Materials Used
H3.3 Applications
4. Choosing Between 3D Printers and Laser Cutters
The choice between a 3D printer and a laser cutter depends on the specific requirements of the project. Here are some factors to consider:
5. Conclusion
3D printers and laser cutters are powerful tools that empower users to create and innovate in various fields. By understanding their capabilities, materials, and applications, users can make informed decisions when choosing the right technology for their projects. Both technologies continue to evolve, promising even more exciting possibilities in the future of manufacturing and design.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between 3D modeling and 3D printing?
A1. 3D modeling involves creating digital 3D models using software, while 3D printing refers to the physical creation of objects based on those digital models.
Q2. Can 3D printers be used for metalworking?
A2. Yes, some 3D printers can use metal powders to create metal parts, known as metal additive manufacturing.
Q3. What is the advantage of using a laser cutter over a traditional saw?
A3. Laser cutters offer higher precision, reduced material waste, and the ability to cut intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with a saw.
Q4. Are 3D printers or laser cutters more expensive?
A4. The cost of 3D printers and laser cutters varies depending on the model and capabilities. Generally, laser cutters tend to be more expensive than entry-level 3D printers.
Q5. What are some safety precautions to follow when using 3D printers and laser cutters?
A5. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions, wear appropriate safety gear (e.g., gloves, safety glasses), and ensure proper ventilation to minimize exposure to fumes or particles.