3D Printing and Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
3D printing and laser cutting are two advanced manufacturing technologies that have revolutionized various industries. 3D printing enables the creation of complex three-dimensional objects from digital designs, while laser cutting involves using a laser to cut or engrave materials. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these technologies, their applications, benefits, and potential future advancements.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Printing and Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1.1 Introduction
- 2 3D Printing
- 2.2 Types of 3D Printing Technologies
- 2.3 Applications of 3D Printing
- 3 3D Printing
- 3.4 What is 3D Printing?
- 3.5 Types of 3D Printing Technologies
- 4 Laser Cutting
- 4.6 What is Laser Cutting?
- 4.7 Types of Laser Cutting Machines
- 4.8 Applications of Laser Cutting
- 5 Comparison of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
- 6 Benefits of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
- 6.9 Benefits of 3D Printing
- 6.10 Benefits of Laser Cutting
- 7 Future Advancements
- 7.11 Advancements in 3D Printing
- 7.12 Advancements in Laser Cutting
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 FAQs
- 9.13 What is the difference between 3D printing and CNC machining?
- 9.14 Can 3D printing be used to produce metal parts?
- 9.15 Is laser cutting suitable for cutting wood?
- 9.16 What is the maximum thickness that laser cutting can handle?
- 9.17 Can laser cutting be used for engraving?
3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects from digital models. It works by depositing layers of material, such as plastic, metal, or ceramic, on top of each other until the desired shape is formed.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, including:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The most common type, where a heated nozzle extrudes molten material onto a build platform.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Uses a laser to fuse powdered material into solid layers.
- Multi-Jet Modeling (MJP): Deposits droplets of liquid resin, which are then cured by UV light.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing and laser cutting are two advanced manufacturing technologies that have revolutionized various industries. 3D printing enables the creation of complex three-dimensional objects from digital designs, while laser cutting involves using a laser to cut or engrave materials. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these technologies, their applications, benefits, and potential future advancements.
- 3d Laser Cut Wood 3D Laser Cut Wood: Unlocking Intricate Designs And Precision Craftsmanship
- 3d Cutting Design 3D Cutting Design: Unleashing Precision And Creativity In Manufacturing
- 3 D Laser Cutting 3D Laser Cutting: A Revolutionary Technology For Precision Manufacturing
- 3d Laser Wood Cutter 3D Laser Wood Cutter: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Printers And Laser Cutters 3D Printers And Laser Cutters: A Comprehensive Guide
3D Printing
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects from digital models. It works by depositing layers of material, such as plastic, metal, or ceramic, on top of each other until the desired shape is formed.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, including:
3D printing has a wide range of applications, including:
- Prototyping: Creating physical models of designs for testing and evaluation.
- Manufacturing: Producing custom parts, tools, and products in small or large quantities.
- Healthcare: Creating prosthetics, implants, and surgical models.
- Art and Design: Producing unique and intricate sculptures, jewelry, and other objects.
Laser Cutting
What is Laser Cutting?
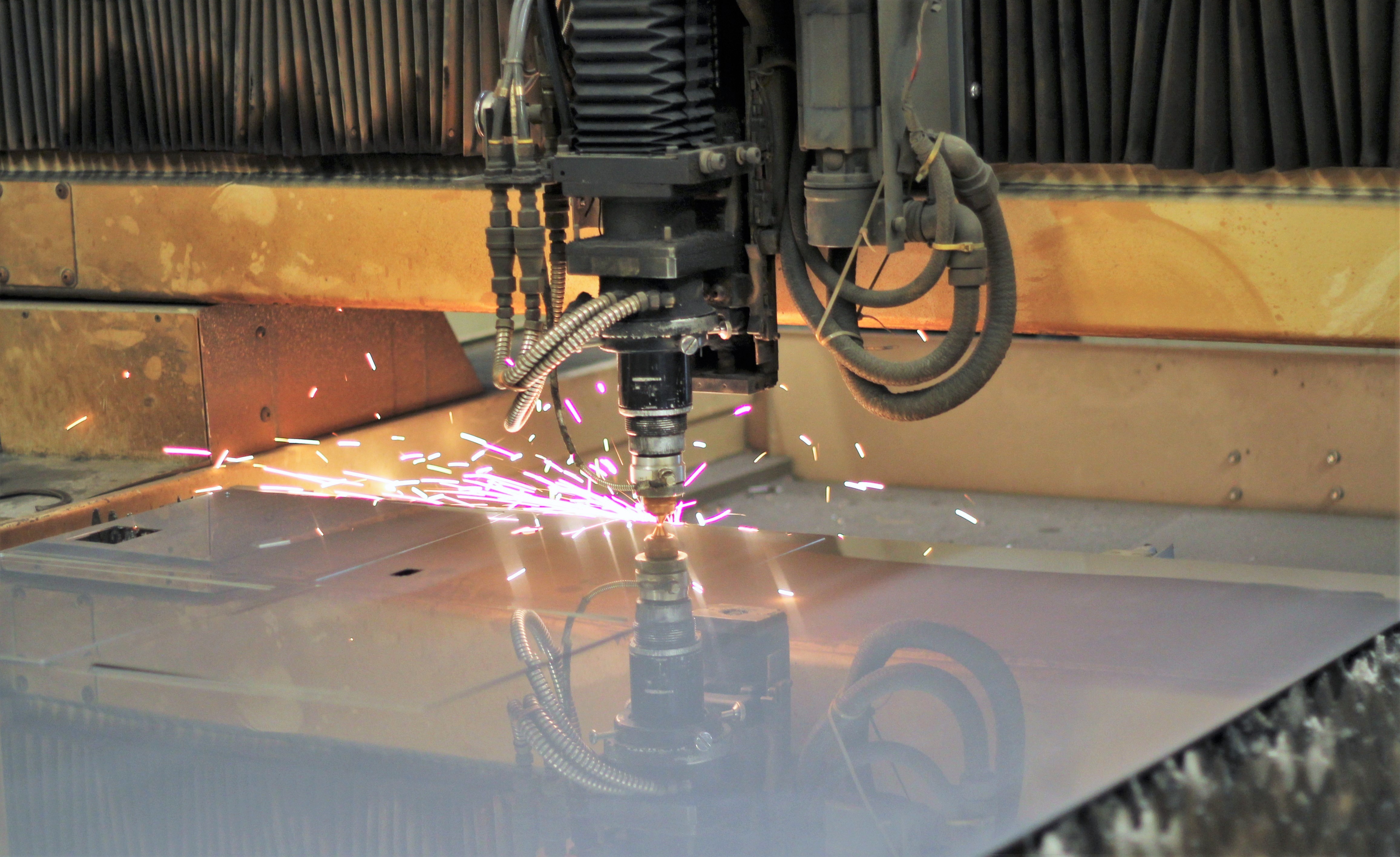
Laser cutting is a process that uses a laser to cut or engrave materials. It involves directing a high-powered laser beam at the material, which melts, burns, or vaporizes it, resulting in precise cuts or engravings.
Types of Laser Cutting Machines
There are different types of laser cutting machines, based on the type of laser used:
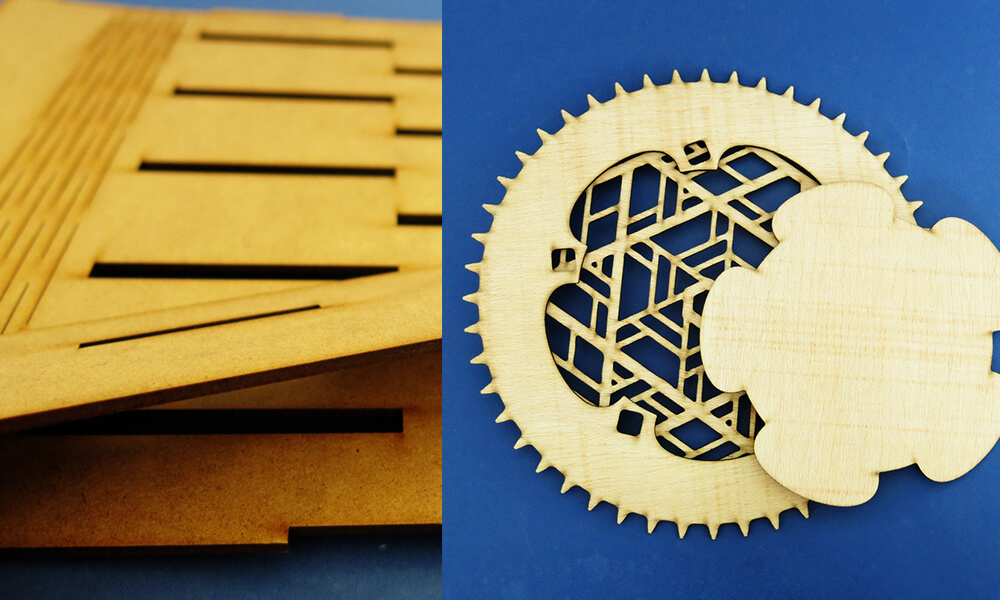
- CO2 Lasers: Commonly used for cutting non-metals like wood, acrylic, and fabrics.
- Fiber Lasers: More powerful and efficient, used for cutting metals and thicker materials.
- Nd:YAG Lasers: Used for precise cutting of delicate materials like glass and ceramics.

Applications of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting has numerous applications, including:
- Industrial Manufacturing: Cutting metal sheets, fabricating parts, and engraving surfaces.
- Signage and Display: Creating custom signs, logos, and display panels.
- Textile Industry: Cutting and engraving fabrics for clothing, upholstery, and home décor.
- Medical Equipment: Manufacturing surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices.
Comparison of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
| Feature | 3D Printing | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Adds material layer by layer | Cuts or engraves material |
| Output | Three-dimensional objects | Two-dimensional cuts or engravings |
| Materials | Plastics, metals, ceramics | Metals, non-metals, glass, ceramics |
| Applications | Prototyping, manufacturing, healthcare, art | Industrial manufacturing, signage, textiles, medical equipment |
| Cost | Varies depending on technology and materials | Relatively low cost |
| Accuracy | Can be high but may depend on technology | High precision and detail |
| Speed | Can be slow, especially for large objects | Faster than 3D printing |
Benefits of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
Benefits of 3D Printing
- Rapid Prototyping: Allows for quick and cost-effective creation of prototypes for testing and design validation.
- Customizable Designs: Enables the production of parts and products with unique shapes and geometries that are difficult to achieve through traditional manufacturing.
- Reduced Costs: Can eliminate the need for tooling and molds, leading to lower production costs, especially for small-batch production.
- Improved Quality: Produces high-quality parts with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
Benefits of Laser Cutting
- Precision Cutting: Delivers accurate and intricate cuts with minimal distortion or burrs.
- Speed and Efficiency: Can cut through materials quickly and efficiently, increasing productivity.
- Versatility: Can cut a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics.
- Non-Contact Process: Does not require physical contact with the material, preventing damage or deformation.
Future Advancements
Advancements in 3D Printing
- Multi-Material Printing: Enables the use of multiple materials in a single print, creating parts with different properties and functionalities.
- Bioprinting: Utilizes 3D printing techniques to create living tissues and organs for medical applications.
- 4D Printing: Introduces the dimension of time, allowing printed objects to change shape or respond to external stimuli.
Advancements in Laser Cutting
- Ultrafast Laser Cutting: Employs high-power, ultrafast lasers to achieve extremely precise and clean cuts.
- Micro Laser Cutting: Enables the cutting of very small and intricate features on materials like glass and semiconductors.
- Hybrid Laser-Plasma Cutting: Combines laser and plasma cutting technologies to enhance cutting speed and efficiency for thicker materials.
Conclusion
3D printing and laser cutting are powerful manufacturing technologies that offer numerous benefits for various industries. 3D printing enables the creation of complex three-dimensional objects, while laser cutting provides precise cutting and engraving capabilities. Both technologies are continuously evolving, with advancements in multi-material printing, bioprinting, and ultrafast laser cutting promising even greater possibilities in the future.
FAQs
What is the difference between 3D printing and CNC machining?
CNC machining subtracts material from a solid block, while 3D printing adds material layer by layer. CNC machining offers higher precision and durability, but 3D printing allows for more complex geometries and faster prototyping.
Can 3D printing be used to produce metal parts?
Yes, metal 3D printing technologies, such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM), allow for the production of high-quality metal parts with intricate designs.
Is laser cutting suitable for cutting wood?
Yes, CO2 lasers are commonly used for cutting and engraving wood, providing precise and clean cuts.
What is the maximum thickness that laser cutting can handle?
The maximum thickness that laser cutting can handle depends on the laser power, material type, and cutting speed. Fiber lasers can cut through thicker materials like steel and aluminum, while CO2 lasers are more suitable for non-metals.
Can laser cutting be used for engraving?
Yes, laser cutting machines can be used for both cutting and engraving. By adjusting the laser power and cutting speed, it is possible to achieve detailed engravings on various materials.