Laser 3D Cutter: A Comprehensive Guide
Laser 3D cutters, also known as laser cutters or laser engraving machines, are versatile tools that have revolutionized various industries, from manufacturing and prototyping to art and design. They use a focused laser beam to cut, engrave, or mark a wide range of materials, including wood, acrylic, metal, and even leather.
H1: Understanding Laser 3D Cutters
Table of Content
- 1 Laser 3D Cutter: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1.1 H1: Understanding Laser 3D Cutters
- 1.2 H2: Materials and Applications
- 1.3 H1: Understanding Laser 3D Cutters
- 1.4 H2: Materials and Applications
- 1.5 H3: Types of Laser 3D Cutters
- 1.6 H2: Features and Considerations
- 1.7 H2: Workflow and Best Practices
- 1.8 H2: Conclusion
- 1.9 FAQs
H2: Laser Technology
H2: Operation
Laser 3D cutters are typically controlled by computer-aided design (CAD) software. The software converts 3D models into cutting paths, which are then executed by the laser cutter. The laser head moves along these paths, delivering the laser beam to the material.
H2: Materials and Applications
Laser 3D cutters can work with a diverse range of materials, including:
- Wood: plywood, MDF, hardwood
- Acrylic: clear, colored, patterned
- Metal: stainless steel, aluminum, brass
- Leather: genuine, synthetic, suede
- Paper: cardstock, chipboard, corrugated cardboard
- Shapeways Laser Cutting Shapeways Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Advanced Manufacturing
- Laser Cutter Comparable To Glowforge Laser Cutter Comparable To Glowforge: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Printing And Laser Cutting 3D Printing And Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d 6 Axis Laser Cutting 3D 6-Axis Laser Cutting: Revolutionizing Complex Fabrication
- 3d Tube Cutting 3D Tube Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Advanced Manufacturing
H1: Understanding Laser 3D Cutters
H2: Laser Technology
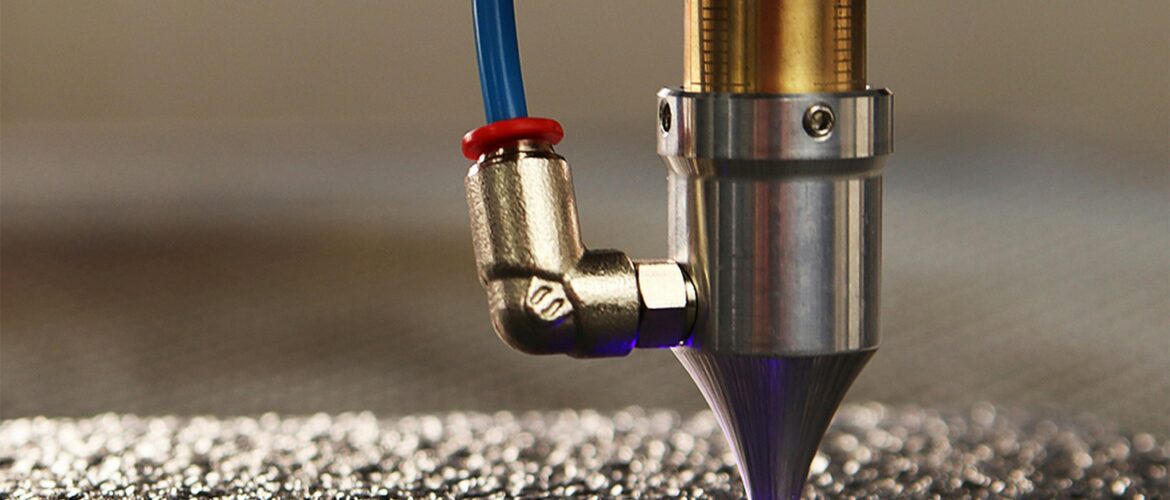
Laser cutters utilize a laser source, typically a carbon dioxide (CO2) or fiber laser, to generate a concentrated beam of light. This beam is then directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to focus it onto the target material. The laser’s high energy density vaporizes or melts the material, resulting in precise cuts or engravings.
H2: Operation
Laser 3D cutters are typically controlled by computer-aided design (CAD) software. The software converts 3D models into cutting paths, which are then executed by the laser cutter. The laser head moves along these paths, delivering the laser beam to the material.
H2: Materials and Applications
These materials find applications in:
- Prototyping and product development
- Art and design projects
- Signage and engraving
- Jewelry and accessories
- Medical devices and tools
H3: Types of Laser 3D Cutters
H4: CO2 Laser Cutters
CO2 laser cutters use a carbon dioxide gas-filled tube to generate the laser beam. They are known for their high power and speed, making them ideal for cutting and engraving thicker materials.
H4: Fiber Laser Cutters
Fiber laser cutters utilize a fiber optic cable to transmit the laser beam. They offer higher precision and efficiency than CO2 lasers and are suitable for fine detail work on metals.
H4: Hybrid Laser Cutters
Hybrid laser cutters combine the advantages of both CO2 and fiber lasers, providing versatility and high performance across a wide range of materials.
H2: Features and Considerations
When selecting a laser 3D cutter, consider the following factors:
- Power: Measured in watts (W), higher power lasers can cut thicker materials and achieve faster speeds.
- Work Area: The maximum size of material that can be cut or engraved.
- Precision: The accuracy and detail of the cuts and engravings.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the cutter is compatible with your CAD software.
- Safety Features: Interlocks, fume extraction, and protective eyewear are essential for safe operation.
H2: Workflow and Best Practices
H3: Design Preparation
Create detailed 3D models using CAD software and ensure they are compatible with the laser cutter’s software.
H3: Material Selection
Choose the appropriate material based on the desired application and the laser cutter’s capabilities.
H3: Laser Parameter Optimization
Adjust laser power, speed, and focus to achieve optimal results for the specific material and thickness.
H3: Safety Precautions
Wear proper safety gear, operate the cutter in a well-ventilated area, and follow all manufacturer’s instructions.
H2: Conclusion
Laser 3D cutters offer unparalleled precision, speed, and versatility for a wide range of cutting and engraving applications. Understanding the technology, materials, and workflow involved is crucial for successful operation. By considering the factors discussed in this guide, you can choose the right laser 3D cutter and optimize its use for your specific needs.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between laser cutting and laser engraving?
A1: Laser cutting vaporizes or melts the material to create cuts, while laser engraving removes a thin layer of material to create surface markings.
Q2: What are the limitations of laser 3D cutters?
A2: They can only cut through a limited material thickness and may not be suitable for highly reflective or transparent materials.
Q3: How can I maintain my laser 3D cutter?
A3: Regular cleaning, lens inspection, and calibration are essential for optimal performance and longevity.