3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
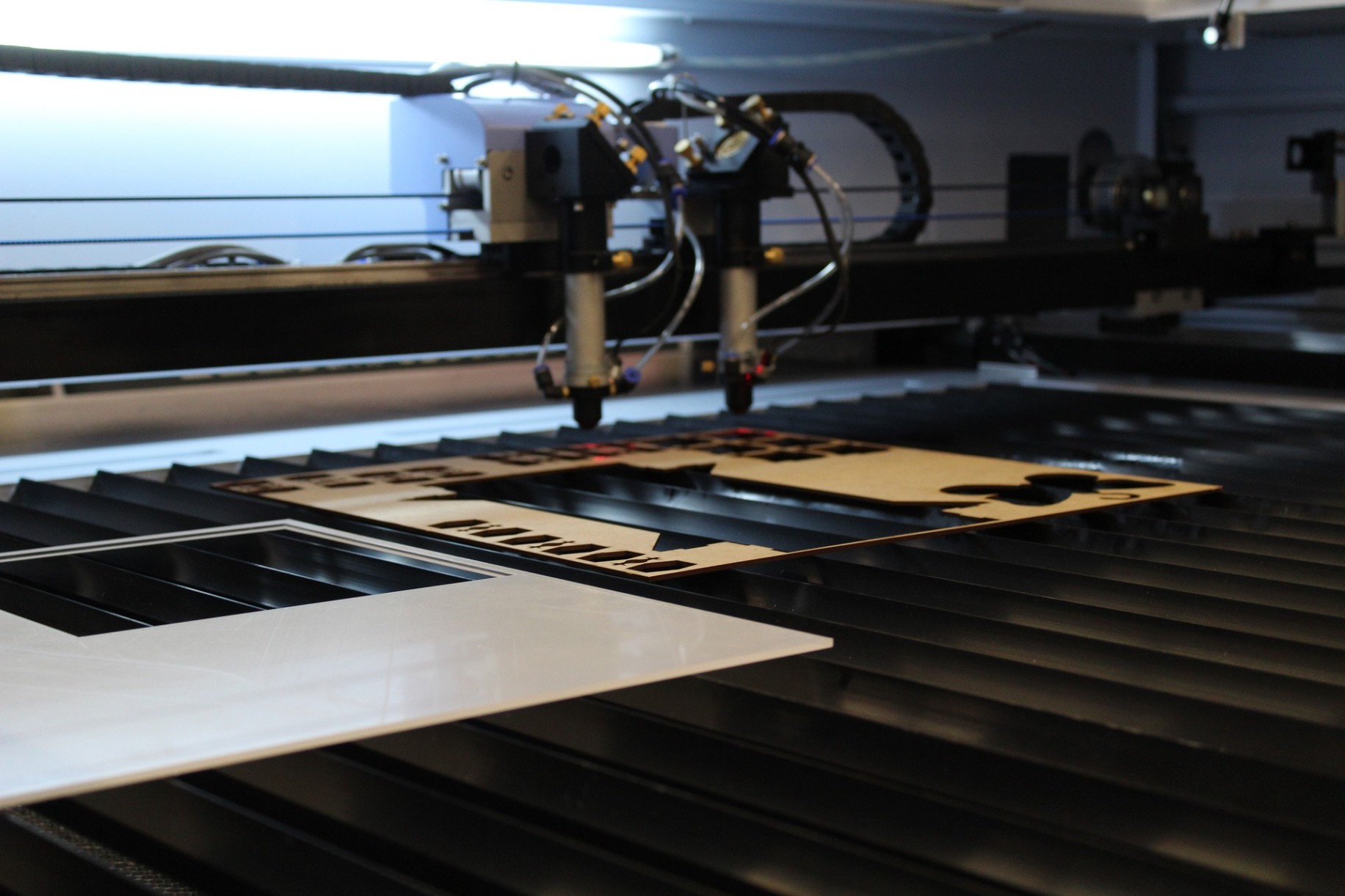
3D laser cutting is a cutting-edge manufacturing technology that utilizes a focused laser beam to precisely cut intricate shapes and designs into various materials. This advanced process offers unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility, making it a game-changer in various industries.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Understanding 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.2.1 Key Components
- 1.3 Advantages of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.4 Understanding 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.4.2 Process Overview
- 1.4.3 Key Components
- 1.5 Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.6 Materials for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.7 Factors Affecting 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.8 Design Considerations for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.9 Conclusion
- 1.10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Understanding 3D Laser Cutting
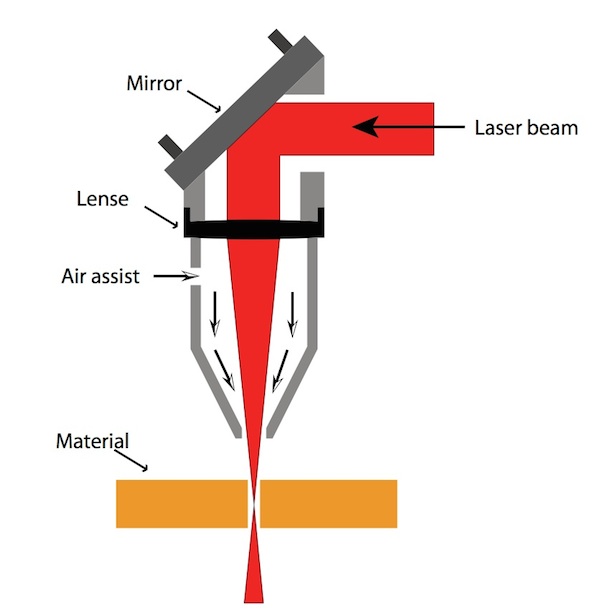
3D laser cutting involves directing a high-power laser beam onto a workpiece, where it vaporizes or melts the material along the desired cutting path. The laser’s precise control allows for complex and detailed cuts, creating intricate 3D structures.
Key Components
The core components of a 3D laser cutting system include:
- Laser source (e.g., CO2, fiber, diode)
- Optical system (e.g., lenses, mirrors)
- CNC control system
- Workpiece positioning system
Advantages of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting is a cutting-edge manufacturing technology that utilizes a focused laser beam to precisely cut intricate shapes and designs into various materials. This advanced process offers unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility, making it a game-changer in various industries.
- Snapmaker Laser Cutting Guide Snapmaker Laser Cutting Guide: A Comprehensive Walkthrough
- Thingiverse Laser Cut Thingiverse Laser Cut: Unleashing The Power Of Digital Fabrication
- 3d Laser Cutting Metal 3D Laser Cutting Metal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Mazak 3d Laser Cutting Mazak 3D Laser Cutting: Revolutionizing Metal Fabrication
- 3d Cnc Cutting Design 3D CNC Cutting Design: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding 3D Laser Cutting
Process Overview
3D laser cutting involves directing a high-power laser beam onto a workpiece, where it vaporizes or melts the material along the desired cutting path. The laser’s precise control allows for complex and detailed cuts, creating intricate 3D structures.
Key Components
The core components of a 3D laser cutting system include:
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser cutting ensures exceptional precision and accuracy, enabling the creation of intricate designs with tight tolerances.
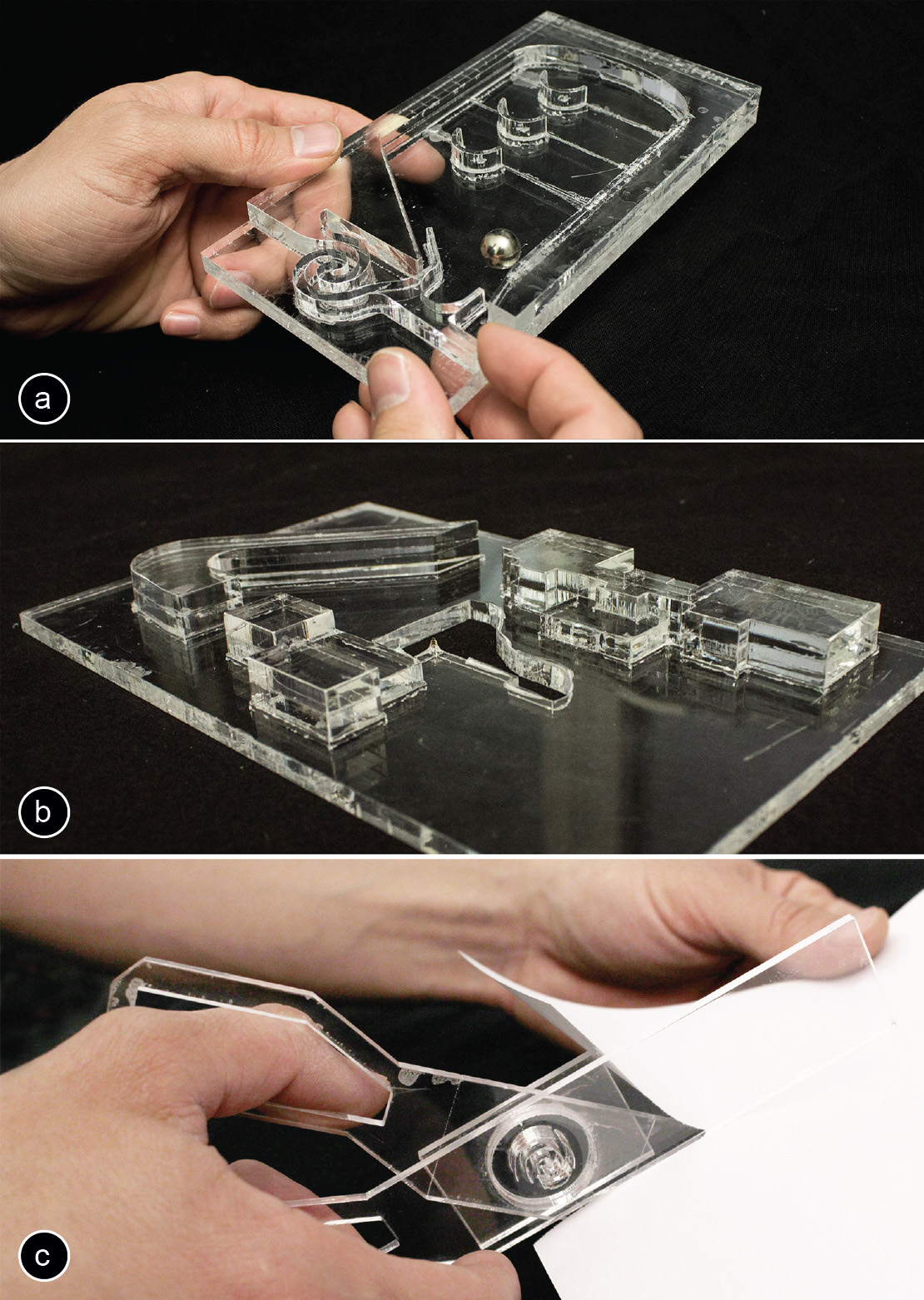
- Versatility: 3D laser cutting can process a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and ceramics.
- High Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting offers high cutting speeds, reducing production time and increasing productivity.
- Non-Contact Process: The laser beam does not physically contact the workpiece, minimizing material deformation and ensuring surface integrity.
- Automation: CNC control systems allow for automated operation, reducing labor costs and improving consistency.
Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting finds applications in a multitude of industries, including:
- Automotive: Creating custom parts, prototypes, and complex shapes for vehicles.
- Aerospace: Manufacturing lightweight and durable components for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Medical: Producing surgical instruments, prosthetics, and other medical devices.
- Electronics: Cutting printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic components with precision.
- Architecture and Design: Creating intricate facades, sculptures, and decorative elements.
Materials for 3D Laser Cutting
The choice of material for 3D laser cutting depends on the specific application and desired properties. Common materials include:
- Metals: Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, copper, brass
- Plastics: Acrylic, polycarbonate, polyethylene, polypropylene
- Wood: Plywood, hardwood, MDF
- Ceramics: Glass, porcelain, tiles
Factors Affecting 3D Laser Cutting
Several factors influence the quality and efficiency of 3D laser cutting:
- Laser Power: Higher laser power enables faster cutting and deeper penetration.
- Laser Wavelength: Different wavelengths are suitable for specific materials and applications.
- Cutting Speed: The speed of the laser beam determines the cut quality and material removal rate.
- Pulse Duration: Shorter pulses result in cleaner cuts, while longer pulses provide more heat input.
- Material Properties: The material’s composition, thickness, and heat conductivity affect the cutting process.
Design Considerations for 3D Laser Cutting
When designing for 3D laser cutting, it is crucial to consider:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen material is compatible with the laser cutting process.
- Geometry Complexity: Complex geometries may require multiple passes or specialized techniques.
- Tolerances: Specify precise tolerances to achieve the desired accuracy.
- Material Thickness: Consider the thickness of the material and adjust the laser parameters accordingly.
- Heat Management: Plan for heat dissipation to prevent material deformation or damage.
Conclusion
3D laser cutting is a transformative technology that empowers manufacturers to create innovative and intricate designs with unparalleled precision and efficiency. Its versatility and wide range of applications make it an indispensable tool for industries ranging from automotive to medical. By understanding the process, materials, and design considerations, manufacturers can harness the full potential of 3D laser cutting to drive innovation and achieve exceptional results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between 3D laser cutting and traditional laser cutting?
A: Traditional laser cutting involves flat-bed cutting, while 3D laser cutting allows for cutting complex 3D shapes.
Q: How does 3D laser cutting achieve such high precision?
A: The precise control of the laser beam and CNC systems enables accurate cutting along complex paths.
Q: What materials are suitable for 3D laser cutting?
A: A wide range of materials can be processed, including metals, plastics, wood, and ceramics.
Q: What are the advantages of 3D laser cutting over other manufacturing methods?
A: Precision, speed, versatility, non-contact operation, and automation are key advantages.
Q: How can I design for 3D laser cutting?
A: Consider material compatibility, geometry complexity, tolerances, material thickness, and heat management when designing for 3D laser cutting.