How to Design 3D Laser Cut Models: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
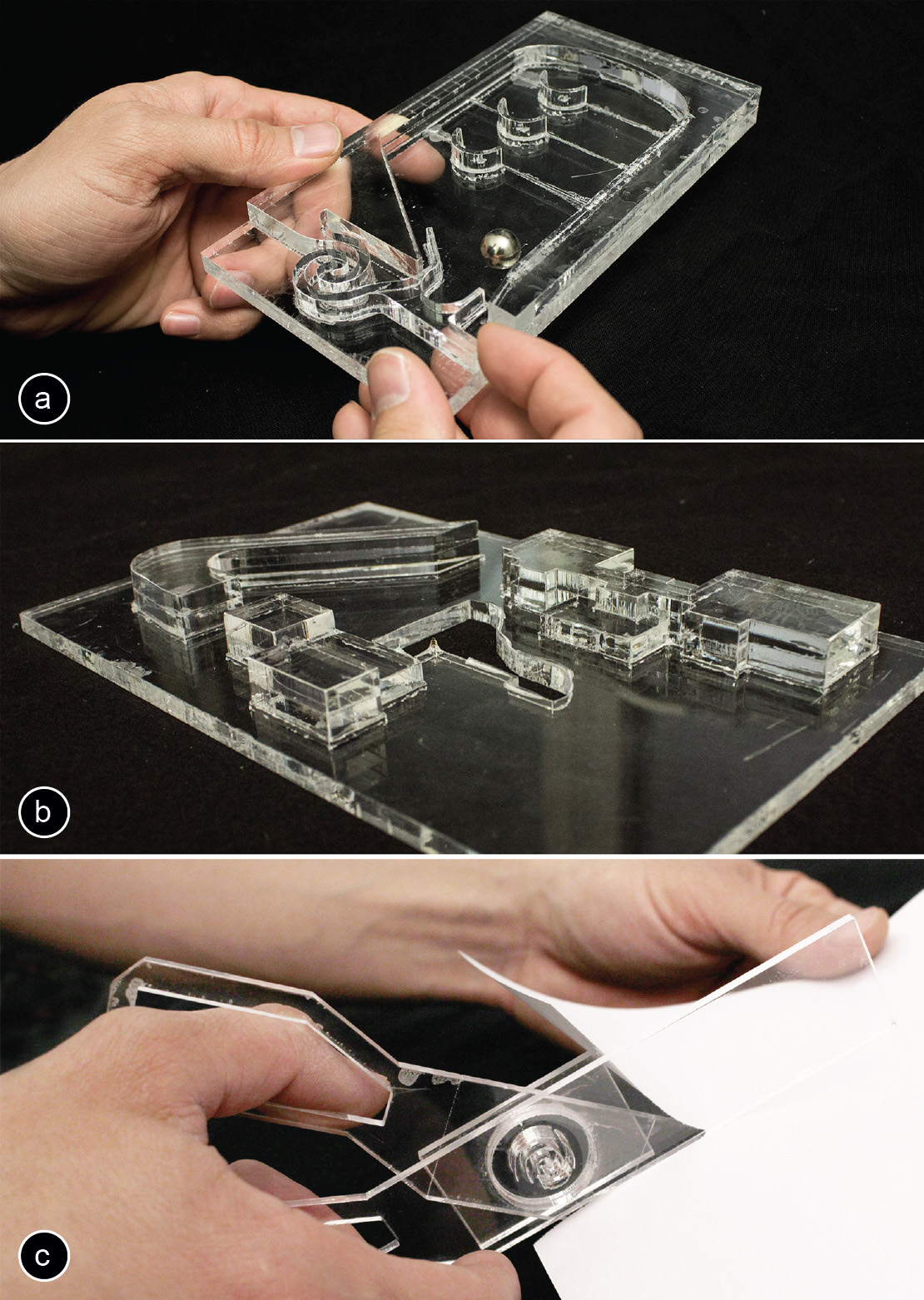
Laser cutting is a versatile manufacturing process that uses a focused beam of laser light to cut or engrave materials with high precision. This technology has revolutionized the design and production of 3D models, enabling the creation of intricate and complex shapes that were previously impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Table of Content
- 1 How to Design 3D Laser Cut Models: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 H1: Design Principles for Laser Cut Models
- 1.3 H1: Software for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.4 H1: Understanding the Basics of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.5 H1: Step-by-Step Guide to Designing 3D Laser Cut Models
- 1.6 H1: Best Practices for 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.7 H1: Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 1.8 H1: Conclusion
- 1.9 FAQs
This article provides a comprehensive guide to designing 3D laser cut models, covering essential concepts, best practices, and step-by-step instructions. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced designer, this guide will empower you to create stunning and functional 3D models using laser cutting.
H2: Laser Cutting Process
Laser cutting involves directing a laser beam through a focused lens onto a material surface. The intense heat generated by the laser vaporizes or melts the material, creating a precise cut or engraving.
H2: Material Selection
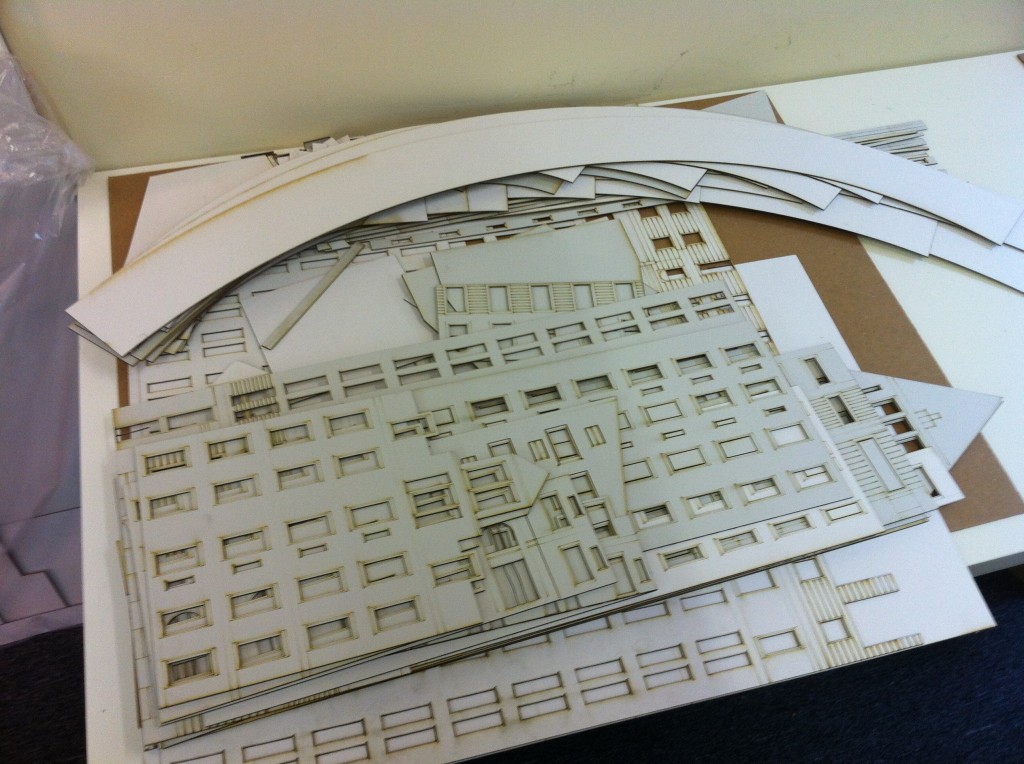
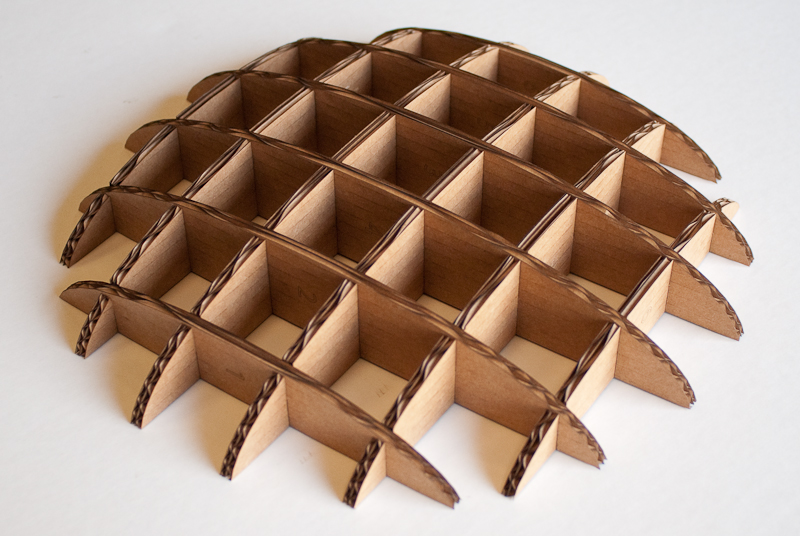
The choice of material plays a crucial role in laser cutting. Common materials used include wood, acrylic, metal, and cardboard. Each material has unique properties that affect the cutting process, such as hardness, thickness, and reflectivity.
H1: Design Principles for Laser Cut Models
H2: Vector vs. Raster Graphics
Laser cutting requires vector graphics, which define shapes using lines and curves, rather than raster graphics, which are composed of pixels. Vector graphics provide crisp and precise cuts, while raster graphics can result in jagged edges.
H2: Kerf and Offset
The kerf is the width of the material removed by the laser cut. It’s important to consider the kerf when designing interlocking or fitting components to ensure proper alignment. The offset refers to the distance between the laser cut line and the original design, which can compensate for the kerf.
H1: Software for 3D Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a versatile manufacturing process that uses a focused beam of laser light to cut or engrave materials with high precision. This technology has revolutionized the design and production of 3D models, enabling the creation of intricate and complex shapes that were previously impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
- 3d Laser Wood Cutter 3D Laser Wood Cutter: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut Files Free 3D Laser Cut Files Free: Unleash Your Creativity
- 3d Laser Cut Christmas Decorations 3D Laser Cut Christmas Decorations: A Festive Touch To Your Holiday Decor
- 3d Wood Laser Cut Art 3D Wood Laser Cut Art: A Comprehensive Guide To Design, Creation, And Applications
- Dxf 3d Laser Cut H1: Unleashing The Power Of DXF 3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
This article provides a comprehensive guide to designing 3D laser cut models, covering essential concepts, best practices, and step-by-step instructions. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced designer, this guide will empower you to create stunning and functional 3D models using laser cutting.
H1: Understanding the Basics of 3D Laser Cutting
H2: Laser Cutting Process
Laser cutting involves directing a laser beam through a focused lens onto a material surface. The intense heat generated by the laser vaporizes or melts the material, creating a precise cut or engraving.
H2: Material Selection
H2: CAD Software
Computer-aided design (CAD) software is used to create 3D models. Popular CAD software for laser cutting include Fusion 360, SolidWorks, and AutoCAD.
H2: Laser Cutting Software
Laser cutting software allows you to import 3D models, generate toolpaths, and control the laser cutting process. Common laser cutting software include LaserCut 5.3, RDWorks, and LightBurn.
H1: Step-by-Step Guide to Designing 3D Laser Cut Models
H2: Create a 3D Model
Use CAD software to create a 3D model of your desired design. Consider the material you’ll be using and the thickness of the material.
H2: Export the Model
Export the 3D model as a vector graphics file, such as SVG or DXF. Ensure that the file is scaled to the desired size.
H2: Import into Laser Cutting Software
Import the vector graphics file into your laser cutting software. Adjust the settings based on the material you’re using and the desired cut quality.
H2: Generate Toolpaths
Generate toolpaths that define the path the laser will follow to cut the material. Optimize the toolpaths for efficiency and minimize waste.
H2: Cut and Assemble
Load the material into the laser cutter and cut the parts according to the toolpaths. Assemble the parts to create your 3D model.
H1: Best Practices for 3D Laser Cutting
H2: Safety Precautions
Always follow safety precautions when operating a laser cutter. Wear appropriate protective gear and ensure proper ventilation.
H2: Material Preparation
Clean and prepare the material before cutting to remove any contaminants. Secure the material firmly to the cutting bed to prevent movement.
H2: Laser Cutting Parameters
Optimize the laser cutting parameters, including power, speed, and focus, based on the material and desired cut quality.
H2: Post-Processing
After cutting, remove any remaining material or debris from the parts. Consider sanding, finishing, or painting the parts to enhance their appearance.
H1: Troubleshooting Common Issues
H2: Jagged Edges
Jagged edges can be caused by incorrect laser cutting parameters, material movement, or excessive kerf. Adjust the parameters, secure the material properly, and consider using a smaller kerf offset.
H2: Burn Marks
Burn marks can occur due to excessive laser power or slow cutting speed. Reduce the laser power or increase the cutting speed to minimize burn marks.
H2: Incorrect Dimensions
Incorrect dimensions can be caused by scaling errors or incorrect toolpaths. Verify the scale of the model and ensure that the toolpaths are generated correctly.
H1: Conclusion
Designing 3D laser cut models involves understanding the basics of laser cutting, applying design principles, utilizing appropriate software, and following best practices. By mastering these concepts, you can create stunning and functional 3D models with precision and efficiency.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between 2D and 3D laser cutting?
A: 2D laser cutting cuts flat materials, while 3D laser cutting cuts materials in three dimensions to create complex shapes.
Q: What materials can be used for 3D laser cutting?
A: Common materials include wood, acrylic, metal, and cardboard. The choice of material depends on the desired properties and application.
Q: Can I design my own 3D laser cut models?
A: Yes, with the help of CAD software and laser cutting software, you can create your own 3D models for laser cutting.
Q: Is laser cutting safe?
A: Laser cutting can be hazardous if not handled properly. Always follow safety precautions, including wearing protective gear and ensuring proper ventilation.