3D Printing and Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, 3D printing and laser cutting have emerged as transformative technologies that are revolutionizing the production of physical objects. These technologies offer unparalleled precision, customization, and versatility, enabling businesses and individuals to create complex designs and prototypes with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Printing and Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 H1: 3D Printing: The Art of Additive Manufacturing
- 1.3 H1: Laser Cutting: Precision Cutting with Light
- 1.4 H1: 3D Printing: The Art of Additive Manufacturing
- 1.5 H1: Applications of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
- 1.6 H1: Benefits of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
- 1.7 H1: Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
- 1.8 H1: Conclusion
- 1.9 FAQs
H1: 3D Printing: The Art of Additive Manufacturing
H2: Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, each with its own advantages and applications:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common 3D printing technology, which uses a heated nozzle to extrude molten plastic filament layer by layer.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin, creating solid objects with smooth surfaces and high precision.
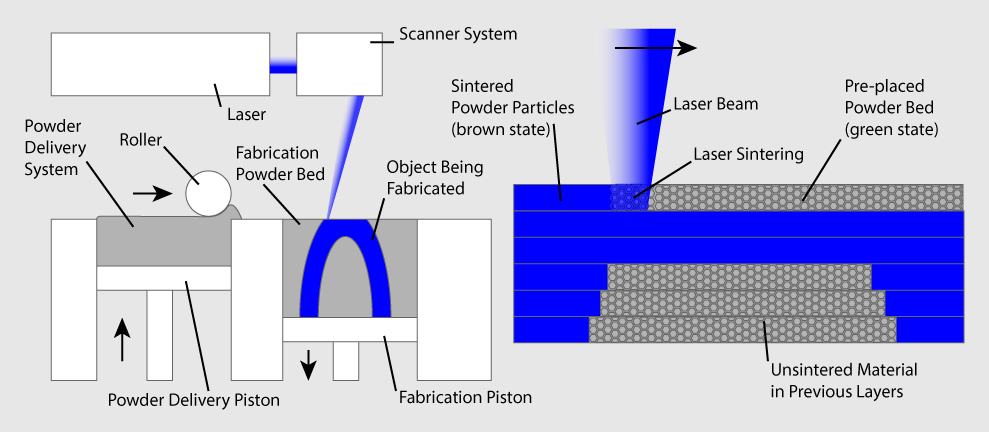
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material, creating durable and complex objects with intricate details.
- Multi-Jet Modeling (MJM): MJM uses multiple inkjet nozzles to deposit droplets of liquid resin, which are then cured by UV light.
H1: Laser Cutting: Precision Cutting with Light
Laser cutting is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses a high-powered laser to cut materials with exceptional accuracy and detail. The laser beam melts, vaporizes, or burns away the material, creating precise cuts and intricate patterns.
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, 3D printing and laser cutting have emerged as transformative technologies that are revolutionizing the production of physical objects. These technologies offer unparalleled precision, customization, and versatility, enabling businesses and individuals to create complex designs and prototypes with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
- 3d Printing With Laser Cut 3D Printing With Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut Car 3D Laser Cut Car: A Comprehensive Guide To Precision And Customization
- 3d Laser Cut Box 3D Laser Cut Box: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut Templates 3D Laser Cut Templates: Unleashing Creativity And Precision
- 3d Models For Laser Cutting 3D Models For Laser Cutting: Unleashing Precision And Creativity
H1: 3D Printing: The Art of Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that involves building three-dimensional objects layer by layer. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods like milling or turning, which remove material to create a desired shape, 3D printing builds objects by adding material in precise layers.
H2: Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, each with its own advantages and applications:
- CO2 Laser Cutters: These use carbon dioxide gas to create a laser beam, suitable for cutting a wide range of materials, including plastics, wood, and metals.
- Fiber Laser Cutters: Fiber lasers use optical fibers to generate a laser beam, offering higher power and faster cutting speeds than CO2 lasers.
- Diode Laser Cutters: Diode lasers are compact and low-power, making them ideal for cutting thin and delicate materials like paper and fabrics.
- Prototyping: Rapid prototyping allows designers and engineers to create physical models of their designs quickly and cost-effectively.
- Custom Manufacturing: 3D printing enables the production of custom parts and products in small batches or one-off pieces.
- Medical Applications: 3D printing is used to create prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools with personalized designs.
- Precision Cutting: Laser cutting offers unmatched precision and accuracy for cutting intricate shapes and designs in various materials.
- Materials Processing: Laser cutting can be used to cut, engrave, mark, and weld a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Laser cutting is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics for cutting complex parts and components.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing significantly reduces the time and cost of creating physical prototypes.
- Design Flexibility: 3D printing enables the creation of complex and organic designs that are difficult or impossible to produce with traditional methods.
- Cost-Effective Production: 3D printing allows for the production of small batches or one-off pieces without the need for expensive tooling or molds.
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser cutting provides exceptional precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of intricate and detailed cuts.
- Versatility: Laser cutting can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, making it suitable for diverse applications.
- Automation: Laser cutting machines can be automated, increasing production efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- Complexity of Design: 3D printing is ideal for complex and organic designs that cannot be easily produced with laser cutting.
- Material Requirements: Consider the materials you need to work with and choose a technology that is compatible with those materials.
- Production Volume: 3D printing is suitable for small batches or one-off pieces, while laser cutting is more efficient for larger production volumes.
- Precision Requirements: Laser cutting offers higher precision and accuracy than 3D printing for cutting intricate shapes and details.
H2: Types of Laser Cutting Machines
Laser cutting machines come in various types, depending on the laser source and power:
H1: Applications of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
3D printing and laser cutting are used in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
H2: Applications of 3D Printing
H2: Applications of Laser Cutting
H1: Benefits of 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
H2: Benefits of 3D Printing
H2: Benefits of Laser Cutting
H1: Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
The choice between 3D printing and laser cutting depends on the specific requirements of your application. Here are some factors to consider:
H1: Conclusion
3D printing and laser cutting are powerful technologies that are transforming the manufacturing industry. They offer unparalleled precision, customization, and versatility, enabling businesses and individuals to create complex designs and prototypes with unprecedented speed and efficiency. By understanding the capabilities and benefits of each technology, you can make informed decisions and leverage these advanced manufacturing techniques to drive innovation and growth in your business.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between 3D printing and laser cutting?
A: 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, while laser cutting uses a laser to cut materials. 3D printing is suitable for creating complex designs, while laser cutting offers higher precision and accuracy.
Q: Which technology is better for prototyping?
A: 3D printing is ideal for rapid prototyping due to its speed and cost-effectiveness.
Q: What materials can be used with 3D printing and laser cutting?
A: 3D printing can be used with plastics, metals, and ceramics. Laser cutting can be used on metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics.
Q: Are 3D printing and laser cutting expensive technologies?
A: The cost of 3D printing and laser cutting machines varies depending on the technology and capabilities. However, both technologies offer cost-effective solutions for prototyping and small-batch production.





.jpg)