Laser Cutting vs. 3D Printing: Unraveling the Differences
Introduction
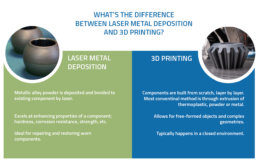
Laser cutting and 3D printing are two advanced manufacturing techniques that have revolutionized various industries. While both processes involve shaping materials, they employ distinct approaches and offer unique advantages. Understanding their differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable technology for specific manufacturing needs.
Table of Content
Laser Cutting
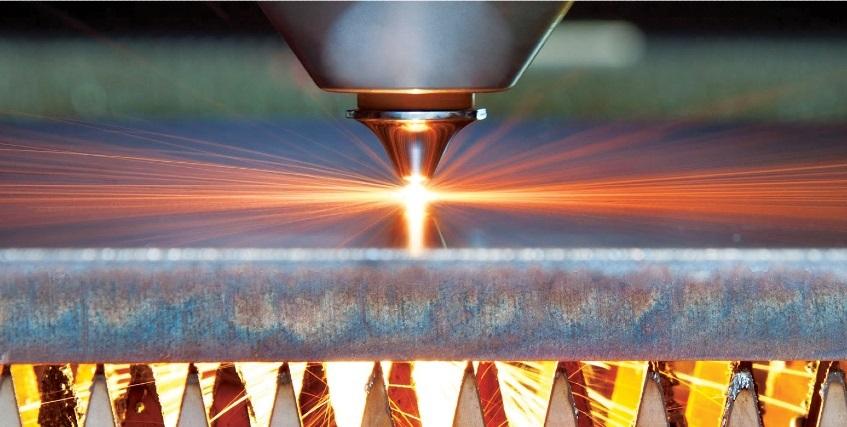
Laser cutting utilizes a concentrated beam of laser energy to cut or engrave materials. The laser beam, typically generated by a CO2 or fiber laser, is precisely directed onto the workpiece, where it melts, vaporizes, or burns the material, creating precise cuts or engravings.
H3: Advantages of Laser Cutting
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser cutting offers exceptional precision, producing sharp and intricate cuts with minimal material distortion.
- Speed and Efficiency: The laser beam’s focused energy enables rapid cutting, making laser cutting an efficient manufacturing process.
- Material Versatility: Laser cutting can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics.
- Low Waste and Environmental Friendliness: Laser cutting generates minimal waste compared to traditional cutting methods, reducing material consumption and environmental impact.
H3: Limitations of Laser Cutting
- 3d Laser Cut Models Download 3D Laser Cut Models Download: A Comprehensive Guide
- Laser Cut Wood 3d Puzzle Laser Cut Wood 3D Puzzle: A Journey Into Precision And Creativity
- Laser Cut 3d Snowflake H1: Laser Cut 3D Snowflake: A Festive And Intricate Holiday Decoration
- 3d Cnc Laser Cutting Machine 3D CNC Laser Cutting Machine: Precision Cutting For Complex Geometries
- 3d Laser Cutting Brisbane 3D Laser Cutting Brisbane: A Comprehensive Guide
- Material Thickness Limitations: Laser cutting is generally limited to thinner materials, typically up to a few millimeters in thickness.
- High Initial Investment: Laser cutting machines require a significant initial investment, which can be a barrier for small businesses or hobbyists.
- Specialized Operator Skills: Operating laser cutting machines requires specialized training and expertise to ensure safety and precision.
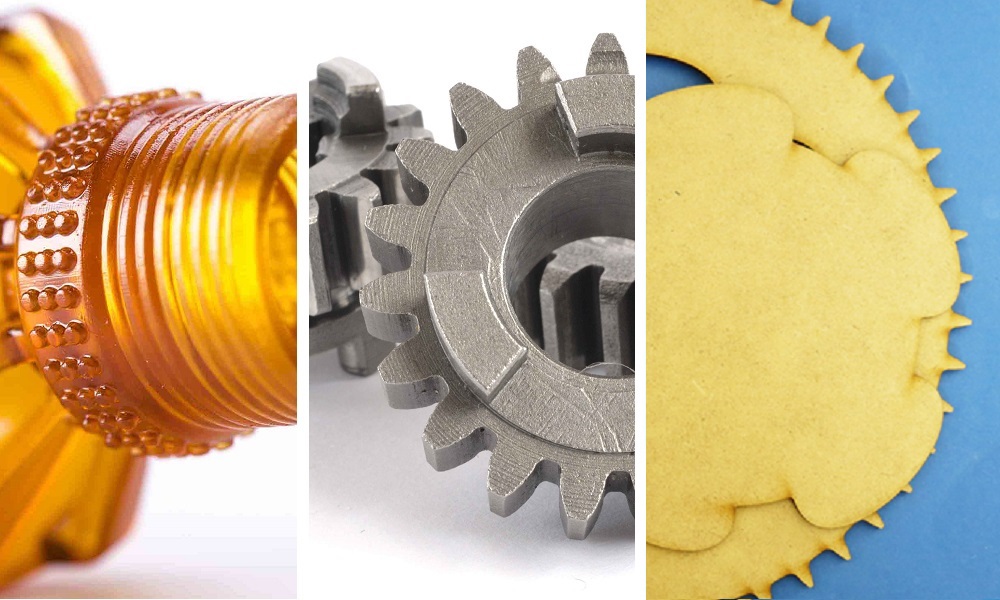
- Complex Geometry: 3D printing allows for the creation of objects with intricate and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Design Flexibility: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and customization, making it ideal for iterative design processes and producing unique or personalized objects.
- Material Variety: 3D printing offers a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites, allowing for tailored properties and functionality.
- Cost-Effective for Small Batches: For small production runs, 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing methods due to reduced tooling costs and material waste.
- Speed and Production Volume: 3D printing can be relatively slow compared to other manufacturing processes, limiting its suitability for mass production.
- Material Strength: While some 3D printing materials offer high strength, they may not match the mechanical properties of materials processed through traditional manufacturing techniques.
- Surface Finish: 3D printed objects may have a rougher surface finish compared to those produced using other methods, requiring additional post-processing steps.
- Laser Cutting: Suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics.
- 3D Printing: Offers a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites.
- Laser Cutting: Offers high precision and sharp cuts, but is limited to thinner materials.
- 3D Printing: Enables the creation of complex geometries, but may have lower precision and surface finish.
- Laser Cutting: Rapid cutting for efficient production of flat or engraved parts.
- 3D Printing: Relatively slower, but suitable for small batches or prototyping.
- Laser Cutting: Requires a significant initial investment and specialized operator skills.
- 3D Printing: Lower initial investment, but ongoing material costs can vary depending on the material and print volume.
- Precision cutting of metal sheets for automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
- Engraving and personalization of signage, jewelry, and promotional items.
- Fabric cutting for apparel, textiles, and upholstery.
- Rapid prototyping and product development for various industries.
- Custom and personalized manufacturing of medical devices, dental prosthetics, and consumer products.
- Architectural and construction models for design visualization and planning.
Laser cutting and 3D printing are two advanced manufacturing techniques that have revolutionized various industries. While both processes involve shaping materials, they employ distinct approaches and offer unique advantages. Understanding their differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable technology for specific manufacturing needs.
Laser Cutting
H2: Principles of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting utilizes a concentrated beam of laser energy to cut or engrave materials. The laser beam, typically generated by a CO2 or fiber laser, is precisely directed onto the workpiece, where it melts, vaporizes, or burns the material, creating precise cuts or engravings.
H3: Advantages of Laser Cutting
3D Printing
H2: Principles of 3D Printing
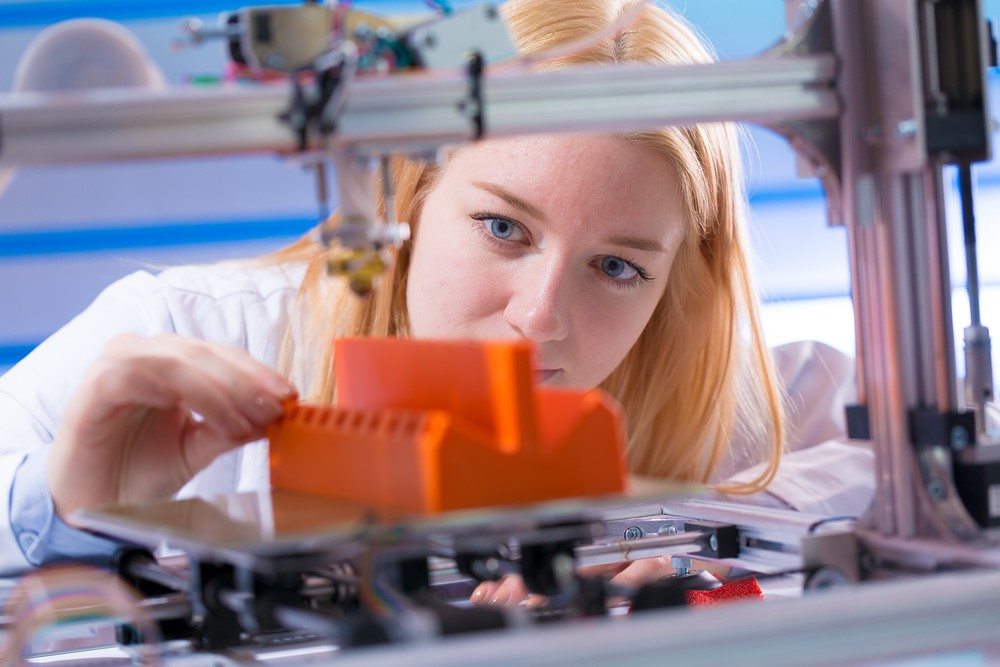
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, builds objects by depositing layers of material upon each other, gradually creating a three-dimensional structure. The material, often in the form of filament, powder, or liquid resin, is fused together through heating, melting, or bonding.
H3: Advantages of 3D Printing

H3: Limitations of 3D Printing
Comparison of Laser Cutting and 3D Printing
H2: Material Considerations
H2: Precision and Complexity
H2: Production Speed and Volume
H2: Cost and Investment
Applications and Industries
H2: Laser Cutting Applications
H2: 3D Printing Applications
Conclusion
Laser cutting and 3D printing are both valuable manufacturing techniques, each offering unique advantages and limitations. Laser cutting excels in precision cutting and engraving, while 3D printing enables the creation of complex geometries and rapid prototyping. Understanding the differences between these technologies allows manufacturers to choose the most appropriate process for their specific requirements, maximizing efficiency and product quality.
FAQs
Q: Which technology is better for mass production?
A: Laser cutting is generally faster and more efficient for mass production of flat or engraved parts.
Q: Can laser cutting be used on glass?
A: Yes, laser cutting can be used on glass with the appropriate laser type and settings.
Q: What is the difference between FDM and SLA 3D printing?
A: FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) uses a thermoplastic filament, while SLA (Stereolithography) uses a liquid resin that is cured by a laser.
Q: Which technology is more environmentally friendly?
A: Both laser cutting and 3D printing can be environmentally friendly, as they generate minimal waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Q: Can 3D printing produce metal parts?
A: Yes, there are metal 3D printing technologies, such as DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) and SLM (Selective Laser Melting), that can produce metal parts directly from CAD designs.