3D Laser Printers: Revolutionizing Additive Manufacturing
Introduction
3D laser printers, also known as laser sintering (LS) systems, have emerged as transformative technologies in the field of additive manufacturing. These advanced printers utilize lasers to fuse powdered materials into complex three-dimensional objects, offering unparalleled precision, accuracy, and material diversity. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of 3D laser printers, exploring their working principles, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Laser Printers: Revolutionizing Additive Manufacturing
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Working Principles of 3D Laser Printers
- 1.3 Applications of 3D Laser Printers
- 1.4 Working Principles of 3D Laser Printers
- 1.5 Benefits of 3D Laser Printers
- 1.6 Future Prospects of 3D Laser Printers
- 1.7 Conclusion
- 1.8 FAQs
Working Principles of 3D Laser Printers
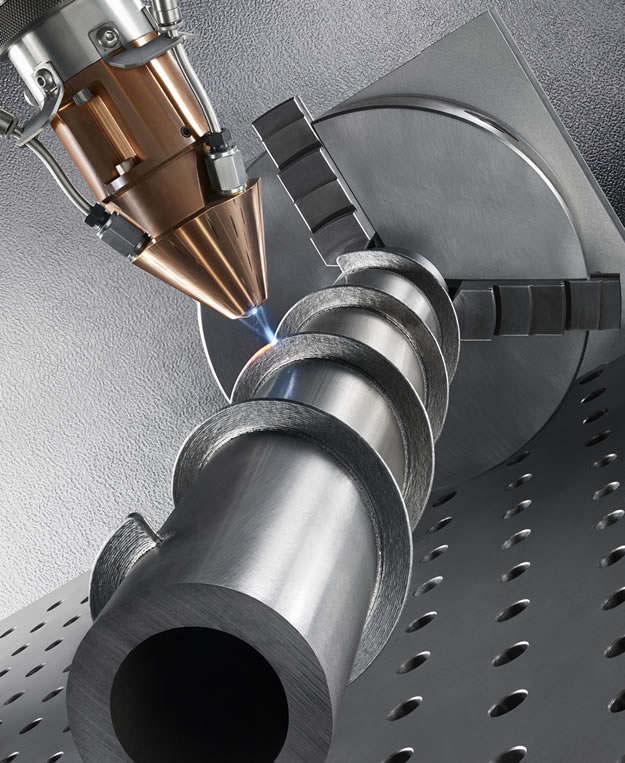
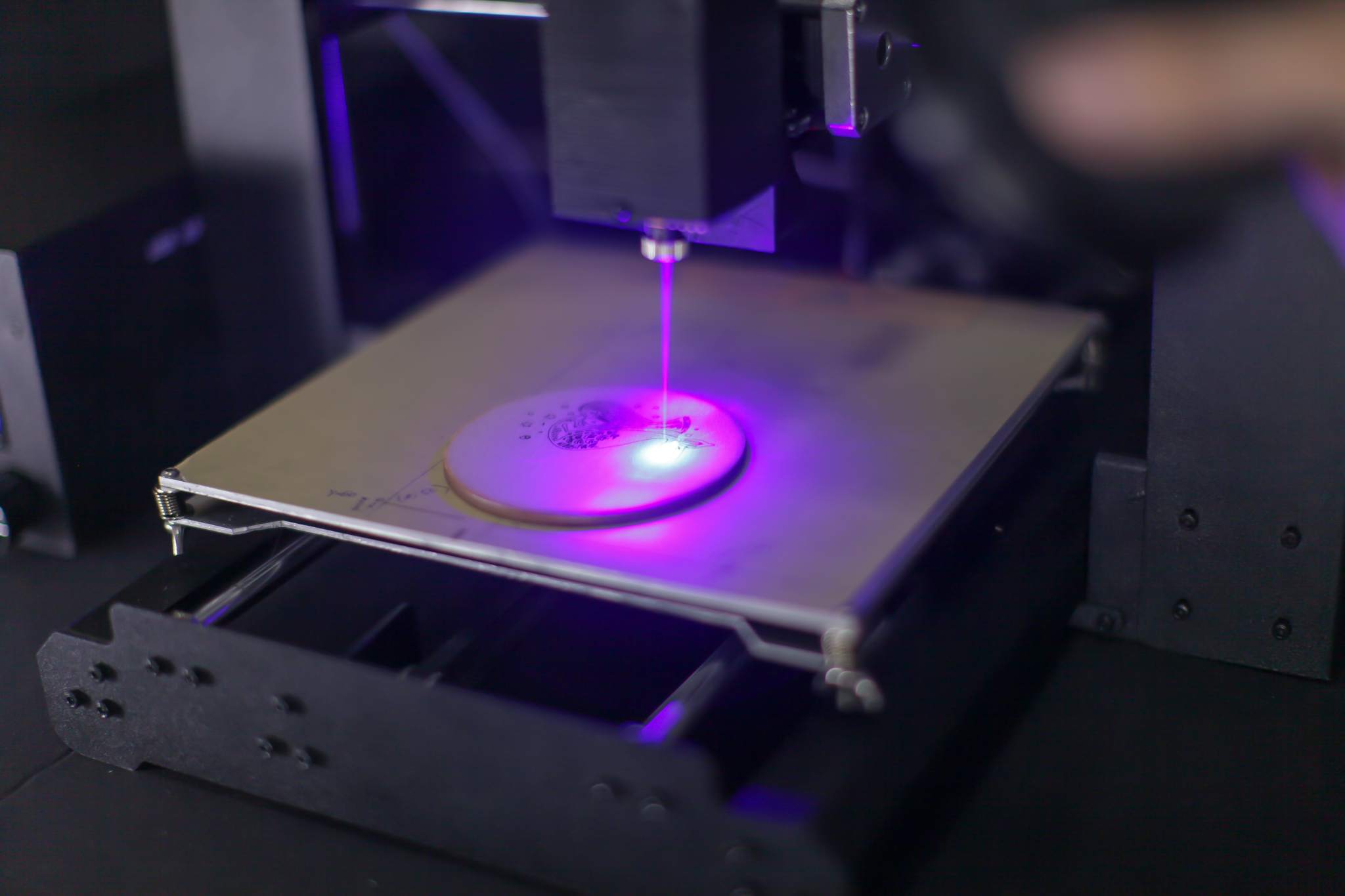
3D laser printers employ a process called laser sintering, where a high-power laser selectively melts or fuses powdered material to create a solid object layer by layer. The laser follows a predefined digital model, precisely controlling the fusion of material and gradually building up the desired shape.
Material Deposition
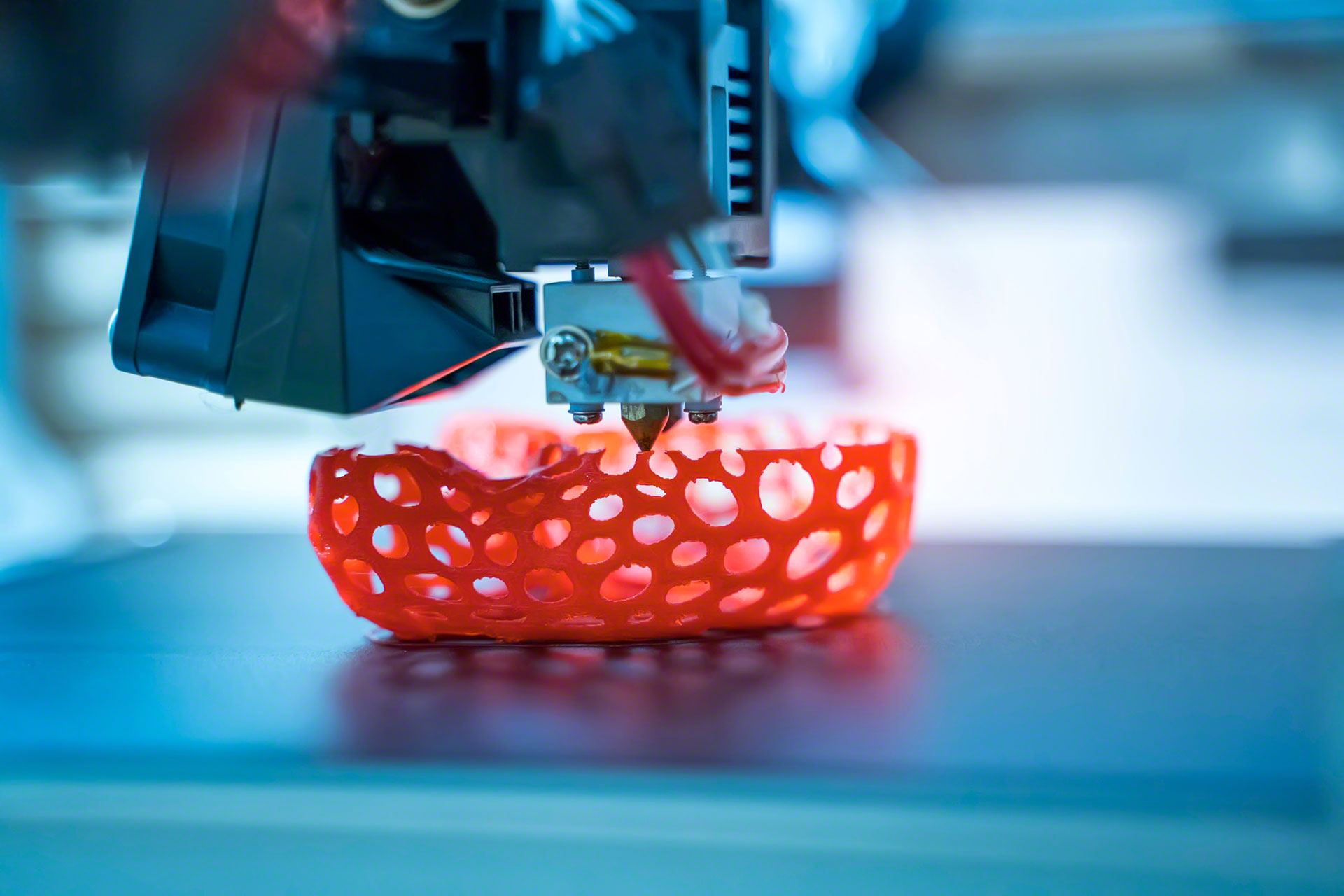
The powdered material used in laser sintering can vary widely, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. The laser selectively fuses these materials, creating strong bonds between particles and resulting in durable and complex objects.
Applications of 3D Laser Printers
Prototyping and Product Development
3D laser printers excel in rapid prototyping, enabling engineers and designers to create functional prototypes quickly and efficiently. This accelerates product development cycles and reduces time-to-market.
Manufacturing of Complex Parts
Laser sintering allows for the production of intricate and complex parts that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods. These parts find applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
Medical Implants and Devices
The ability to create customized medical implants and devices using 3D laser printers has revolutionized healthcare. These implants can be tailored to individual patient anatomy, improving surgical outcomes and patient recovery.
3D laser printers, also known as laser sintering (LS) systems, have emerged as transformative technologies in the field of additive manufacturing. These advanced printers utilize lasers to fuse powdered materials into complex three-dimensional objects, offering unparalleled precision, accuracy, and material diversity. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of 3D laser printers, exploring their working principles, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
- 3d And Laser Cut 3D And Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
- 3d Laser Cut Butterfly 3D Laser Cut Butterfly: An Intricate And Delicate Work Of Art
- 3d Laser Cut Templates Free 3D Laser Cut Templates Free: Unleash Your Creativity With Precision
- 3d Laser Cut Metal Puzzle 3D Laser Cut Metal Puzzles: A Journey Into Intricate Craftsmanship And Intellectual Stimulation
- 3d Laser Cutting Sydney 3D Laser Cutting Sydney: A Comprehensive Guide
Working Principles of 3D Laser Printers
Laser Sintering Process
3D laser printers employ a process called laser sintering, where a high-power laser selectively melts or fuses powdered material to create a solid object layer by layer. The laser follows a predefined digital model, precisely controlling the fusion of material and gradually building up the desired shape.
Material Deposition
The powdered material used in laser sintering can vary widely, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. The laser selectively fuses these materials, creating strong bonds between particles and resulting in durable and complex objects.
Benefits of 3D Laser Printers
High Precision and Accuracy
Laser sintering provides exceptional precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of parts with intricate details and tight tolerances.
Material Diversity
3D laser printers offer a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics, enabling the production of parts with diverse properties and applications.
Rapid Prototyping
Laser sintering significantly reduces prototyping lead times, allowing engineers and designers to iterate and refine designs quickly and cost-effectively.
Complex Geometry
3D laser printers can create objects with complex geometries that are impossible or impractical to manufacture using traditional methods.
Future Prospects of 3D Laser Printers
Advanced Materials
Research and development efforts are focused on developing new and improved materials for laser sintering, expanding the range of applications and properties available.
Increased Speed and Efficiency
Continuous advancements in laser technology and software optimization are expected to increase the speed and efficiency of 3D laser printers, further enhancing their productivity.
Integration with Other Technologies
The integration of 3D laser printing with other technologies, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and digital manufacturing, is expected to streamline workflows and improve the overall manufacturing process.
Conclusion
3D laser printers have revolutionized additive manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, accuracy, material diversity, and the ability to create complex geometries. Their applications extend across various industries, including prototyping, manufacturing, healthcare, and beyond. As technology continues to advance, 3D laser printers are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing and innovation.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between 3D laser printing and fused deposition modeling (FDM)?
A: FDM extrudes molten material layer by layer, while laser sintering fuses powdered material using a laser. Laser sintering offers higher precision and accuracy and allows for a wider range of materials.
Q: What types of materials can be used in 3D laser printers?
A: 3D laser printers can process a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. The choice of material depends on the specific application and desired properties.
Q: Are 3D laser printers suitable for mass production?
A: While 3D laser printers are not currently suitable for mass production of high-volume parts, they are increasingly used for low-volume production of complex and customized parts.