3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Manufacturing
Introduction
3D laser cutting, a groundbreaking technology, has revolutionized various industries, enabling the creation of complex and intricate parts with unmatched precision and efficiency. This article delves into the world of 3D laser cutting, exploring its principles, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
Table of Content
- 1 3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Manufacturing
- 1.1 Introduction
- 2 What is 3D Laser Cutting?
- 2.2 Principles of 3D Laser Cutting
- 3 Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
- 4 What is 3D Laser Cutting?
- 4.3 Principles of 3D Laser Cutting
- 5 Benefits of 3D Laser Cutting
- 6 Considerations for 3D Laser Cutting
- 7 Future of 3D Laser Cutting
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 FAQs
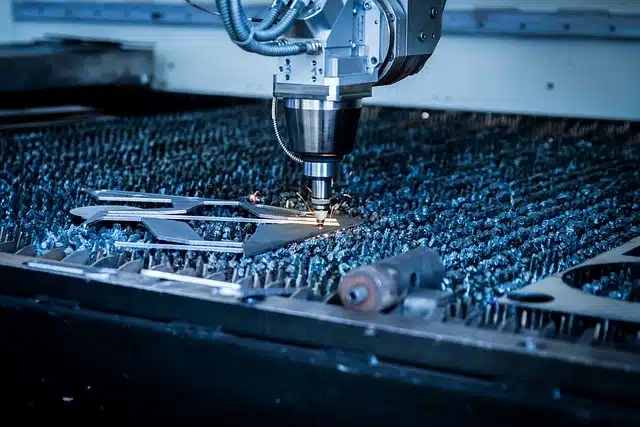
What is 3D Laser Cutting?
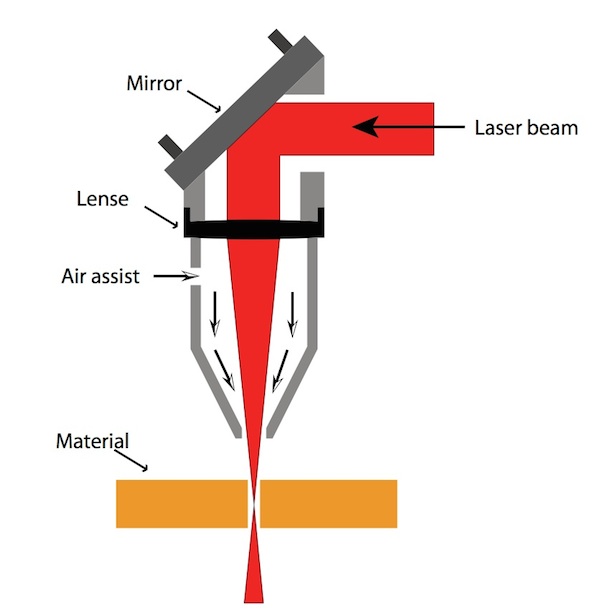
Principles of 3D Laser Cutting
The principles of 3D laser cutting involve:
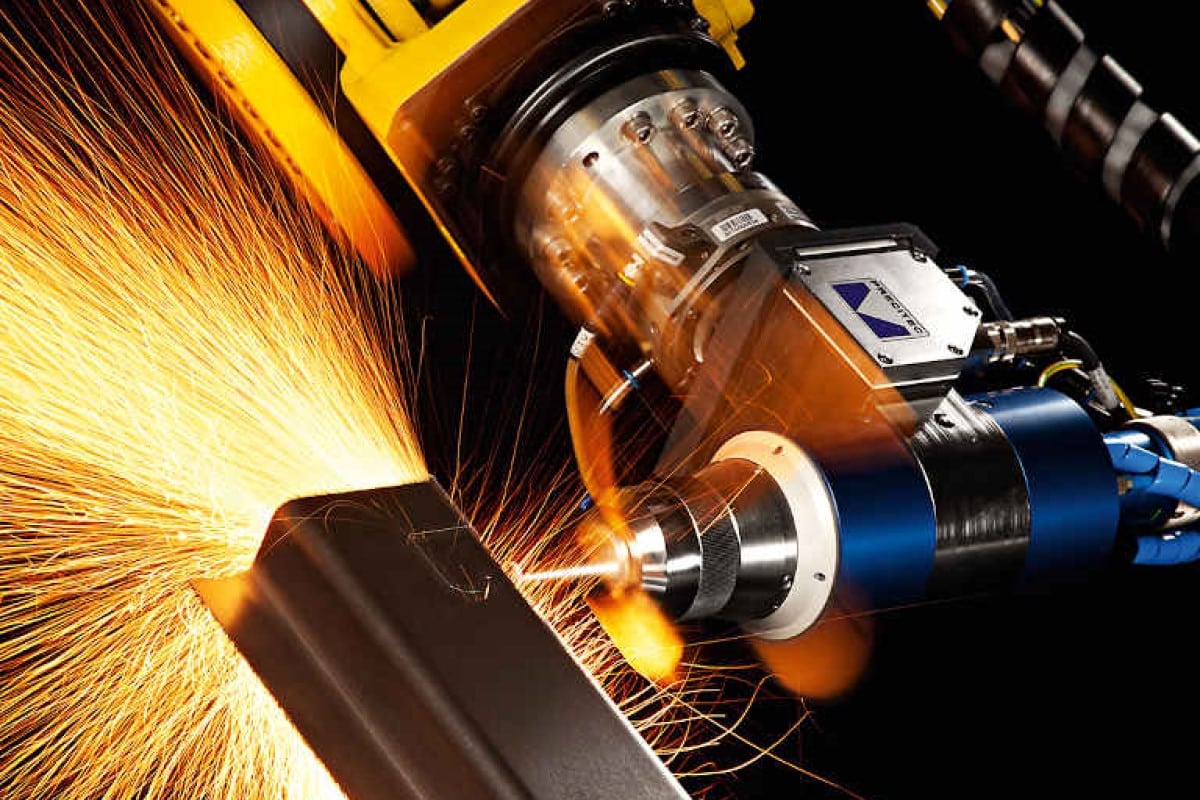
- Laser Generation: A laser source generates a high-power laser beam that is focused and directed towards the workpiece.
- Material Interaction: The laser beam interacts with the material, causing it to vaporize or melt.
- Material Removal: The vaporized or molten material is expelled from the workpiece, leaving behind the desired cut shape.
- Computer Control: Computer-aided design (CAD) software controls the laser beam’s path, ensuring precise and repeatable cuts.
Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting finds applications in numerous industries, including:
3D laser cutting, a groundbreaking technology, has revolutionized various industries, enabling the creation of complex and intricate parts with unmatched precision and efficiency. This article delves into the world of 3D laser cutting, exploring its principles, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
- 3d Laser Cut Lace Fabric 3D Laser Cut Lace Fabric: A Revolution In Textile Design
- Laser Cut 3d Drucken Laser Cut 3D Printing: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut Uk 3D Laser Cutting UK: The Ultimate Guide To Precision Manufacturing
- 3d Puzzle Wooden 3D Puzzle Wooden: A Journey Into The Realm Of Intricate Craftsmanship
- 3d Laser Cut Metal Models 3D Laser Cut Metal Models: A Comprehensive Guide To Precision And Creativity
What is 3D Laser Cutting?
3D laser cutting, also known as laser-induced material removal, is a process that uses a focused laser beam to selectively remove material from a workpiece, resulting in the creation of three-dimensional objects. The laser beam, typically generated by a fiber or CO2 laser source, is guided by computer-controlled software to trace the desired cutting path, vaporizing or melting the material along its path.
Principles of 3D Laser Cutting
The principles of 3D laser cutting involve:
- Aerospace: Fabrication of lightweight and complex aircraft components
- Automotive: Production of intricate parts for engines, transmissions, and body panels
- Medical: Manufacturing of medical devices, prosthetics, and surgical instruments
- Consumer Products: Creation of custom-designed jewelry, toys, and decorative items
- Prototyping and Design: Rapid prototyping and development of functional prototypes
- Precision and Accuracy: The laser beam’s narrow focus and computer control enable highly precise and accurate cuts.
- Complexity: 3D laser cutting can create intricate and complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting is a fast and efficient process, reducing production time and costs.
- Material Versatility: 3D laser cutting can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites.
- Minimal Waste: Laser cutting generates minimal waste, making it an environmentally friendly process.
- Material Properties: The material’s thickness, hardness, and reflectivity can affect the laser cutting process.
- Laser Power and Focus: The laser power and focus determine the cutting speed, accuracy, and edge quality.
- Assist Gases: Inert gases, such as nitrogen or argon, are often used to assist the laser cutting process, improving cut quality and preventing oxidation.
- Equipment and Software: The type of laser cutting machine and software used can influence the overall performance and capabilities.
- Ultrafast Lasers: Ultrafast lasers with pulse durations in the femtosecond range enable precision cutting of even the most delicate materials.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered systems can optimize laser cutting parameters, improve cut quality, and reduce waste.
- Automation and Robotics: Automated laser cutting systems with robotic arms enhance efficiency and reduce manual labor.

Benefits of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
Considerations for 3D Laser Cutting
When considering 3D laser cutting, several factors should be taken into account:
Future of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting technology is continuously evolving, with advancements in laser sources, software, and automation. Future developments include:
Conclusion
3D laser cutting has emerged as a transformative technology that has revolutionized manufacturing across various industries. Its precision, complexity, speed, and material versatility make it an indispensable tool for creating intricate and functional parts. As technology continues to advance, 3D laser cutting is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between 3D laser cutting and 2D laser cutting?
2D laser cutting creates flat shapes, while 3D laser cutting produces three-dimensional objects.
2. What materials can be laser cut in 3D?
A wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites, can be laser cut in 3D.
3. Is 3D laser cutting expensive?
The cost of 3D laser cutting varies depending on factors such as material, complexity, and volume. However, it is generally more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing methods for small to medium-sized production runs.
4. What are the environmental benefits of 3D laser cutting?
3D laser cutting generates minimal waste and uses less energy than traditional manufacturing processes.
5. What is the future of 3D laser cutting?
Future advancements in laser sources, software, and automation will continue to enhance the capabilities and efficiency of 3D laser cutting technology.