Laser Cut 3D Printing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Laser cut 3D printing is a cutting-edge technology that combines laser cutting with 3D printing to create intricate and precise three-dimensional objects. This innovative process offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, making it a highly sought-after technique in various industries.
Table of Content
- 1 Laser Cut 3D Printing: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 H1: Understanding Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.3 H2: Advantages of Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.4 H3: Applications of Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.5 H1: Understanding Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.6 H2: Advantages of Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.7 H4: Materials for Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.8 H5: Design Considerations for Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.9 H6: Post-Processing for Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.10 H7: Trends and Future Prospects of Laser Cut 3D Printing
- 1.11 Conclusion
- 1.12 FAQs
H1: Understanding Laser Cut 3D Printing
H2: Advantages of Laser Cut 3D Printing
1. Intricate Designs: Laser cut 3D printing enables the creation of highly complex and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods.
2. Precision and Accuracy: The computer-controlled laser beam ensures precise cuts and shapes, resulting in high-quality and consistent parts.
3. Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting is a fast and efficient process, making it suitable for large-scale production.
4. Material Versatility: Laser cut 3D printing can be used with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood.
5. Cost-Effectiveness: Laser cutting eliminates the need for expensive tooling and molds, reducing overall production costs.
H3: Applications of Laser Cut 3D Printing
Laser cut 3D printing has found widespread applications across various industries, including:
1. Automotive: Prototyping, interior components, and exterior parts
2. Aerospace: Lightweight and durable components for aircraft and spacecraft
Laser cut 3D printing is a cutting-edge technology that combines laser cutting with 3D printing to create intricate and precise three-dimensional objects. This innovative process offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, making it a highly sought-after technique in various industries.
- Mazak 3d Laser Cutting Mazak 3D Laser Cutting: Revolutionizing Metal Fabrication
- 3d Laser Cut Butterfly Framed Print 3D Laser Cut Butterfly Framed Print: An Exquisite Wall Art Masterpiece
- Anycubic Mega Pro Laser Cutting Anycubic Mega Pro: A Comprehensive Guide To Laser Cutting Precision
- 3d Tube Cutting 3D Tube Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Advanced Manufacturing
- 3d Cutting Design 3D Cutting Design: Unleashing Precision And Creativity In Manufacturing
H1: Understanding Laser Cut 3D Printing
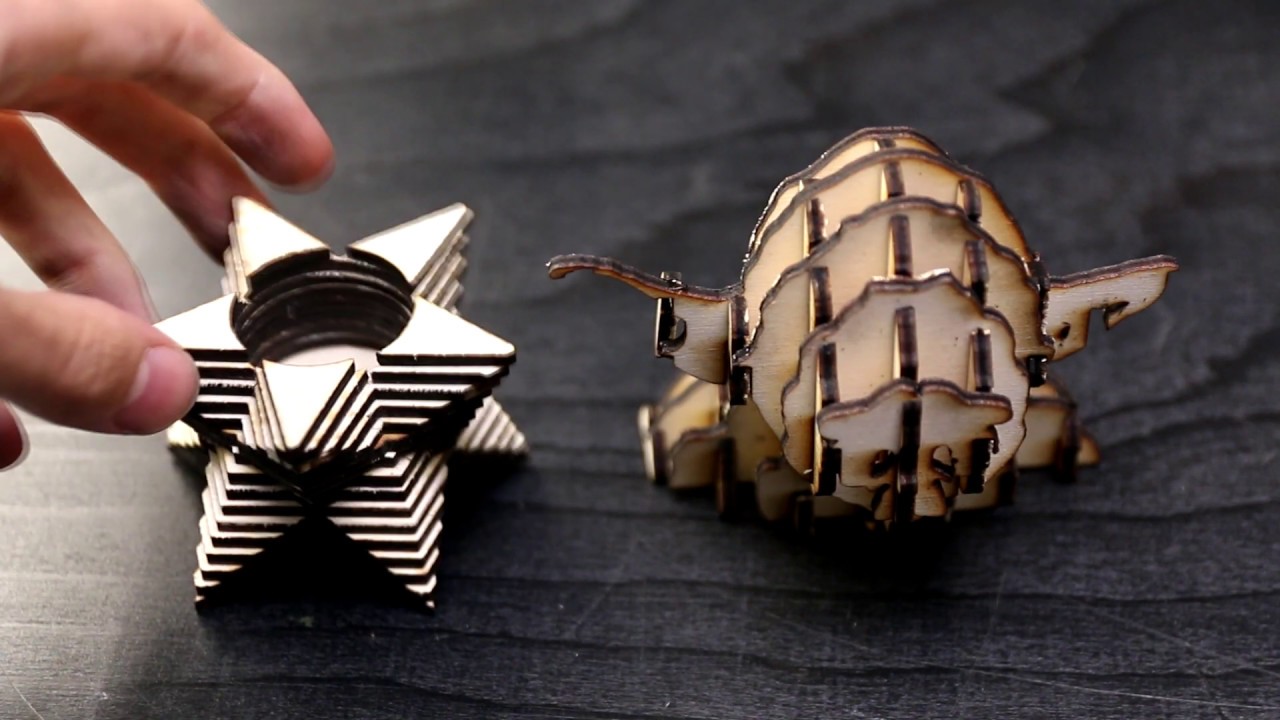
Laser cut 3D printing involves using a laser beam to cut and shape materials into complex forms, which are then stacked and fused together to create a 3D object. The laser beam is directed by a computer-aided design (CAD) file, ensuring accuracy and precision throughout the process.
H2: Advantages of Laser Cut 3D Printing
1. Intricate Designs: Laser cut 3D printing enables the creation of highly complex and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods.
2. Precision and Accuracy: The computer-controlled laser beam ensures precise cuts and shapes, resulting in high-quality and consistent parts.
3. Medical: Implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics
4. Electronics: Circuit boards, enclosures, and connectors
5. Architecture: Models, mock-ups, and decorative elements
H4: Materials for Laser Cut 3D Printing
The choice of materials for laser cut 3D printing depends on the specific application and desired properties. Common materials include:
1. Metals: Steel, aluminum, titanium, and stainless steel
2. Plastics: ABS, PLA, PETG, and nylon
3. Wood: Plywood, MDF, and hardwoods
H5: Design Considerations for Laser Cut 3D Printing
When designing for laser cut 3D printing, it is important to consider the following factors:
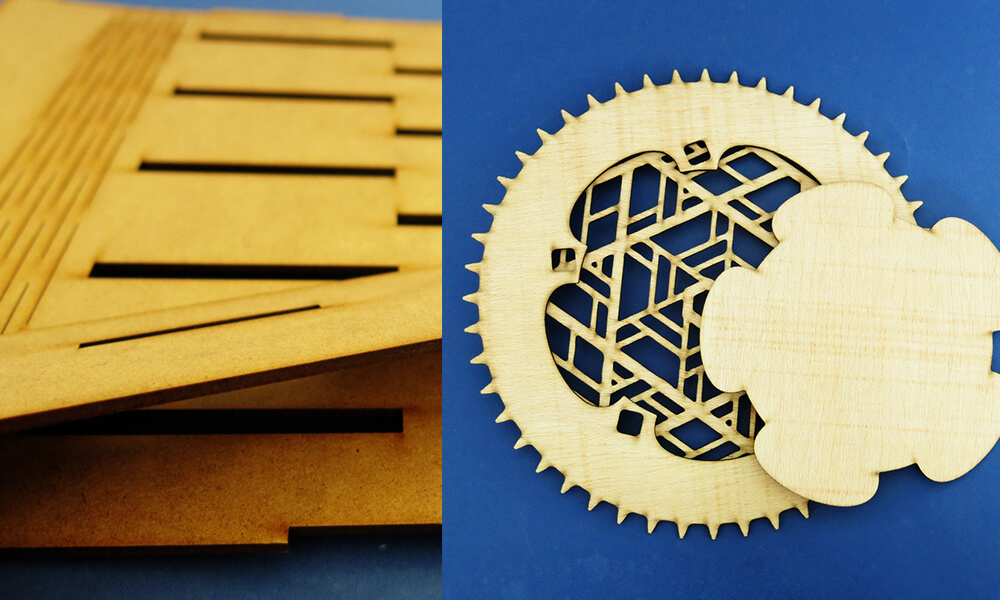
1. Material Thickness: The laser beam can cut through materials of varying thicknesses, but it is essential to select the appropriate thickness for the desired application.
2. Kerf Width: The kerf width refers to the width of the material removed by the laser beam. This needs to be considered when designing joints and interlocking parts.
3. Stacking and Bonding: The parts need to be stacked and bonded together securely to create the final 3D object. Different bonding methods, such as adhesives or welding, can be employed.
H6: Post-Processing for Laser Cut 3D Printing
After laser cutting, post-processing steps may be necessary to enhance the quality and functionality of the parts. These steps include:
1. Deburring: Removing any burrs or sharp edges created during laser cutting.
2. Finishing: Applying surface treatments such as painting, powder coating, or anodizing to improve aesthetics and durability.
3. Assembly: Assembling the individual parts to create the final 3D object.
H7: Trends and Future Prospects of Laser Cut 3D Printing
Laser cut 3D printing is a rapidly evolving technology with numerous promising developments on the horizon. Key trends include:
1. Advanced Materials: The development of new materials specifically designed for laser cut 3D printing will expand its applications.
2. Automated Processes: Increased automation in the laser cutting and assembly processes will improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
3. Multi-Material Printing: The ability to print with multiple materials in a single process will enable the creation of objects with complex properties.
Conclusion
Laser cut 3D printing is a transformative technology that offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. Its ability to create intricate designs, achieve high precision, and reduce production costs makes it a valuable tool for various industries. As the technology continues to advance, it is expected to play an increasingly significant role in the future of manufacturing and product development.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between laser cutting and 3D printing?
Laser cutting involves cutting and shaping materials using a laser beam, while 3D printing builds objects by depositing material layer by layer. Laser cut 3D printing combines these two techniques to create complex 3D structures.
2. What types of materials can be used for laser cut 3D printing?
A wide range of materials can be used, including metals, plastics, and wood. The choice of material depends on the specific application and desired properties.
3. How accurate is laser cut 3D printing?
Laser cut 3D printing offers high precision and accuracy due to the computer-controlled laser beam. The precision is typically in the range of microns.
4. What are the post-processing steps involved in laser cut 3D printing?
Post-processing steps may include deburring, finishing, and assembly to enhance the quality and functionality of the parts.
5. What are the future prospects for laser cut 3D printing?
The future of laser cut 3D printing is bright, with advancements in materials, automated processes, and multi-material printing expected to drive its growth and applications.