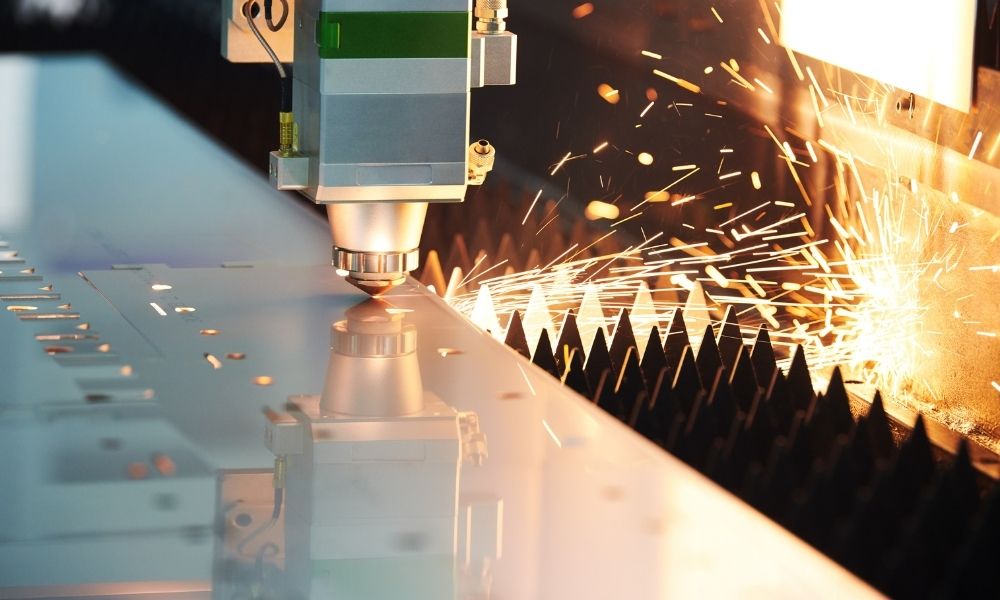
Laser Cut Model: Unlocking Precision and Versatility in Manufacturing
Introduction
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, precision, speed, and customization are paramount. Laser cutting technology has emerged as a game-changer, offering unparalleled capabilities for creating intricate and precise models with exceptional detail. This article delves into the world of laser cut models, exploring their advantages, applications, and the transformative impact they have on various industries.
Table of Content
- 1 Laser Cut Model: Unlocking Precision and Versatility in Manufacturing
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 H1: Advantages of Laser Cut Models
- 1.3 H2: Applications of Laser Cut Models
- 1.4 H1: Advantages of Laser Cut Models
- 1.5 H3: Materials for Laser Cutting
- 1.6 H4: Design Considerations for Laser Cut Models
- 1.7 H5: Software for Laser Cutting
- 1.8 Conclusion
- 1.9 FAQs
H1: Advantages of Laser Cut Models
- Precision: Laser cutters utilize high-powered lasers to cut materials with extreme accuracy, ensuring consistent and precise results.
- Speed: Laser cutting machines operate at high speeds, enabling rapid production of models without compromising quality.
- Flexibility: Laser cutters can cut a wide range of materials, including wood, metal, acrylic, and fabric, providing designers with endless possibilities for model creation.
- Intricate Designs: Laser cutting allows for the creation of complex and intricate designs that would be challenging or impossible to produce using traditional methods.
- Durability: Laser cut models are highly durable and resistant to wear and tear, ensuring their longevity and reliability.
H2: Applications of Laser Cut Models
Laser cut models find widespread application in various industries:
- 3d Laser Cutting Machine 3D Laser Cutting Machine: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cutting Acrylic 3D Laser Cutting Acrylic: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut Wall Art 3D Laser Cut Wall Art: A Stunning Addition To Your Home Decor
- Shapeways Laser Cutting Shapeways Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide To Advanced Manufacturing
- 3d Cnc Laser Cutting Machine 3D CNC Laser Cutting Machine: Precision Cutting For Complex Geometries
- Precision: Laser cutters utilize high-powered lasers to cut materials with extreme accuracy, ensuring consistent and precise results.
- Speed: Laser cutting machines operate at high speeds, enabling rapid production of models without compromising quality.
- Architecture: Laser cut models are used to create scale models of buildings, interiors, and landscapes, providing architects and designers with a tangible representation of their designs.
- Engineering: Laser cut models serve as prototypes for new products, allowing engineers to test and refine designs before full-scale production.
- Art and Design: Laser cut models are employed in artistic creations, such as sculptures, jewelry, and home decor, offering unique and eye-catching designs.
- Education: Laser cut models are valuable educational tools, providing students with hands-on experience in design, engineering, and manufacturing.
- Prototyping: Laser cut models are ideal for rapid prototyping, enabling designers and engineers to quickly iterate and refine their designs.
- Wood: Plywood, MDF, and balsa wood are popular choices for laser cutting due to their ease of cutting and versatility.
- Metal: Stainless steel, aluminum, and brass are commonly used for creating durable and precise metal models.
- Acrylic: Acrylic is a lightweight and transparent material suitable for creating clear and detailed models.
- Fabric: Laser cutting can be used to cut and engrave fabrics, creating intricate designs for clothing, accessories, and home textiles.
- Other Materials: Laser cutters can also cut and engrave materials such as leather, cork, and paper, expanding the possibilities for model creation.
- Material Thickness: The thickness of the material will determine the laser power and cutting speed required.
- Design Complexity: Intricate designs may require multiple passes or specialized cutting techniques.
- Joint Types: Laser cutters can create various joint types, such as butt joints, lap joints, and finger joints, to assemble models.
- Tolerances: Laser cutting can achieve high precision, but tolerances should be considered when designing interlocking parts.
- Surface Finish: Laser cutting can produce smooth or textured surfaces depending on the material and cutting parameters.
- LightBurn: A user-friendly software with a wide range of features for laser cutting, engraving, and etching.
- LaserGRBL: An open-source software compatible with various laser cutters and engraving machines.
- Fusion 360: A comprehensive CAD/CAM software that includes laser cutting capabilities.
- CorelDRAW: A popular graphic design software that can be used for creating laser cutting designs.
- Adobe Illustrator: A vector graphics software that can export designs for laser cutting.
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, precision, speed, and customization are paramount. Laser cutting technology has emerged as a game-changer, offering unparalleled capabilities for creating intricate and precise models with exceptional detail. This article delves into the world of laser cut models, exploring their advantages, applications, and the transformative impact they have on various industries.
H1: Advantages of Laser Cut Models
Laser cutting technology provides a host of benefits that make it an ideal solution for model making:
H3: Materials for Laser Cutting
Laser cutters can work with a diverse range of materials, including:

H4: Design Considerations for Laser Cut Models
When designing models for laser cutting, several factors should be considered:
H5: Software for Laser Cutting
Laser cutting machines are typically controlled by specialized software that allows users to create and import designs, adjust cutting parameters, and monitor the cutting process. Popular laser cutting software includes:
Conclusion
Laser cut models revolutionize the manufacturing industry by providing unprecedented precision, speed, and versatility. Their applications span across various fields, including architecture, engineering, art, education, and prototyping. By carefully considering design parameters and utilizing appropriate materials and software, designers and engineers can create intricate and durable models that meet their specific requirements. Laser cutting technology continues to evolve, promising even greater possibilities for innovation and creativity in the future.
FAQs
Q: What are the advantages of laser cutting over traditional methods?
A: Laser cutting offers higher precision, faster speeds, greater flexibility, and the ability to create intricate designs.
Q: What materials can be laser cut?
A: Laser cutters can cut a wide range of materials, including wood, metal, acrylic, fabric, and leather.
Q: What software is used for laser cutting?
A: Popular laser cutting software includes LightBurn, LaserGRBL, Fusion 360, CorelDRAW, and Adobe Illustrator.
Q: What factors should be considered when designing models for laser cutting?
A: Material thickness, design complexity, joint types, tolerances, and surface finish should all be taken into account.
Q: What industries use laser cut models?
A: Laser cut models find applications in architecture, engineering, art, education, prototyping, and many other industries.