Laser Cutting and 3D Printing: A Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Introduction
Laser cutting and 3D printing are two revolutionary manufacturing technologies that have transformed the way products are designed, produced, and customized. These technologies offer unparalleled precision, flexibility, and speed, enabling the creation of complex and intricate parts, prototypes, and finished goods.
Table of Content
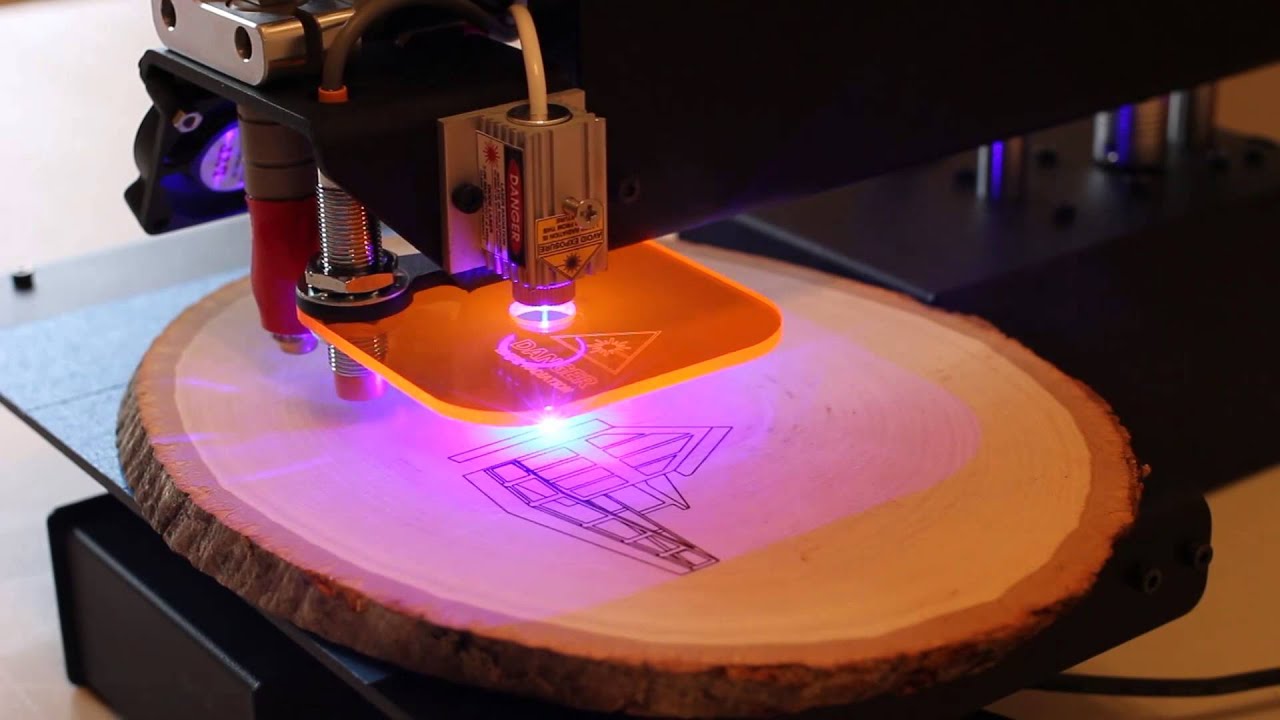
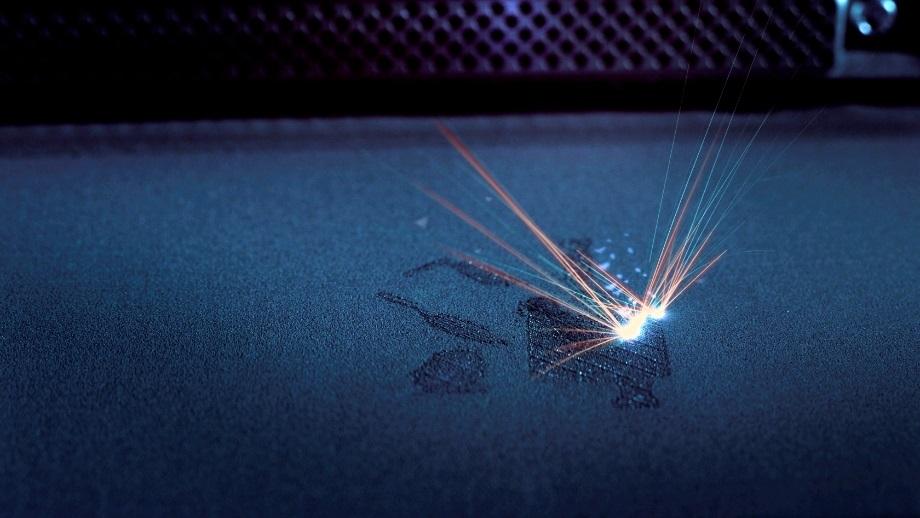
Laser Cutting
H2: Advantages of Laser Cutting
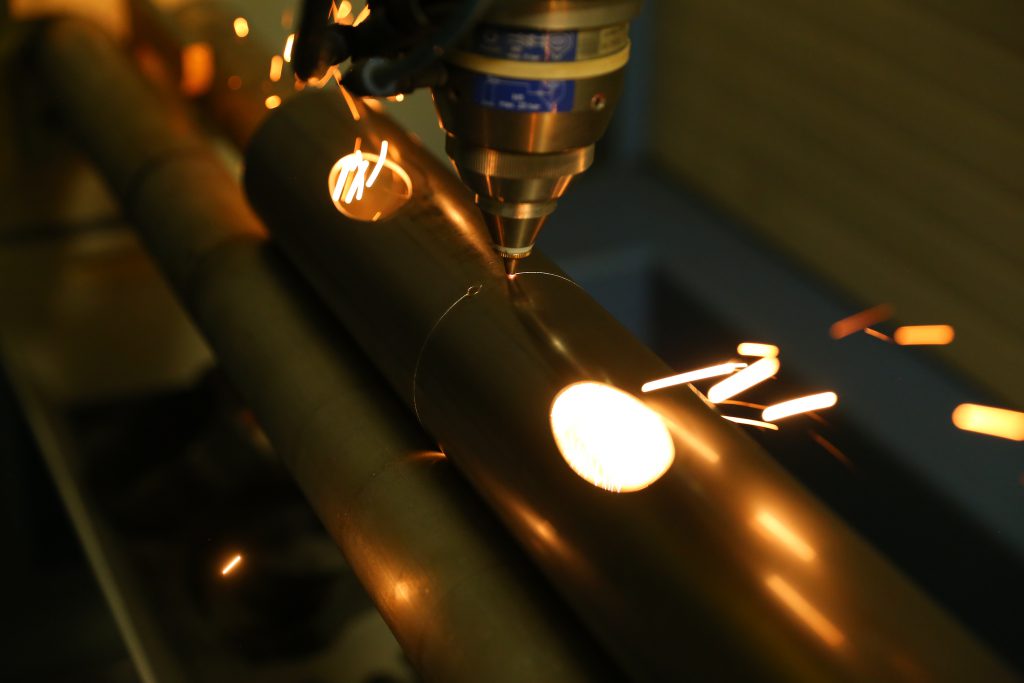
- Precision: Laser cutting provides highly precise cuts with tolerances down to 0.001 inches.
- Speed: Laser cutting is a fast and efficient process, allowing for high-volume production.
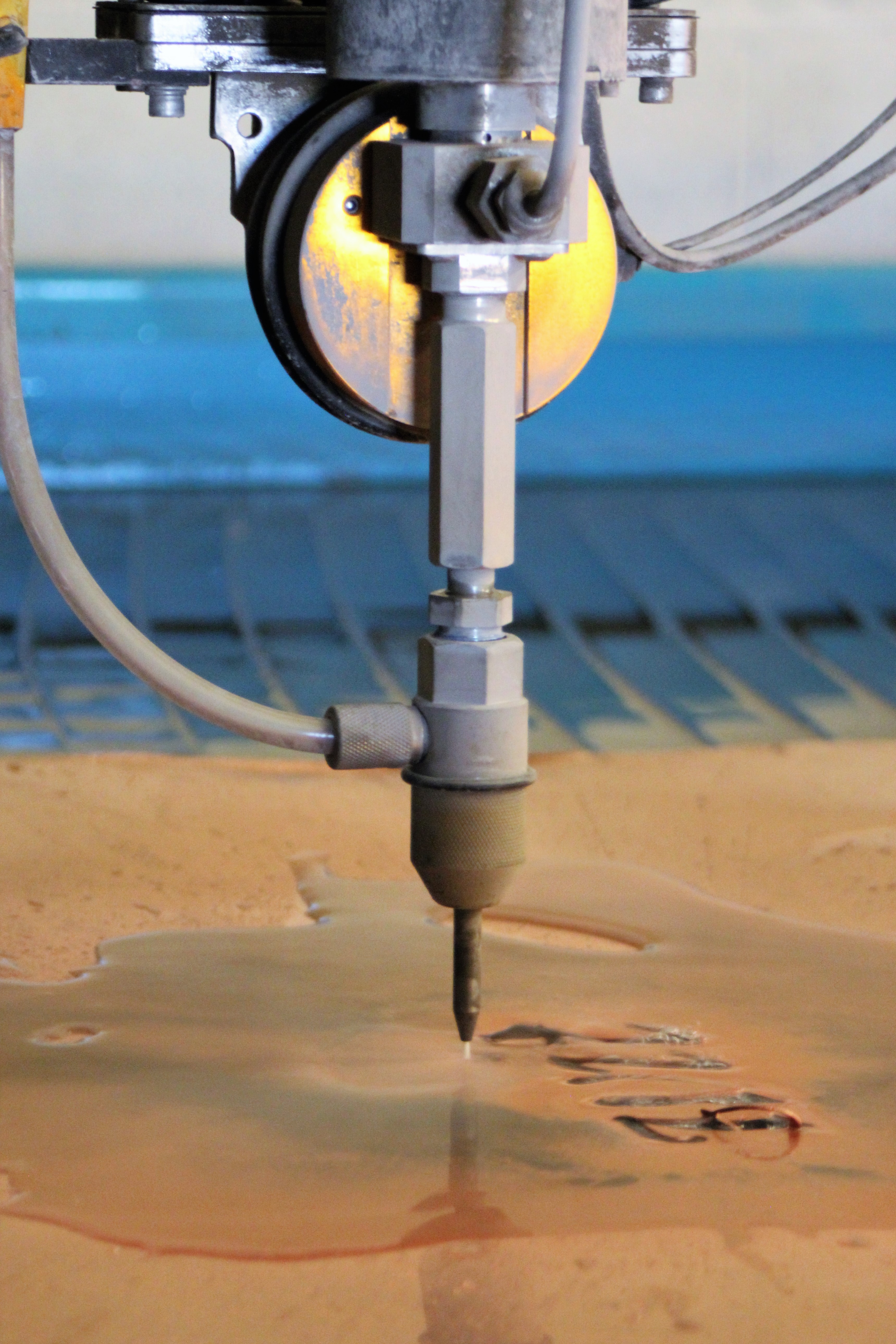
- Versatility: Laser cutting can process a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites.
- Flexibility: Laser cutting machines can be programmed to create complex shapes and patterns.
- Minimal Heat-Affected Zone: Laser cutting generates minimal heat, reducing distortion and warping of the material.
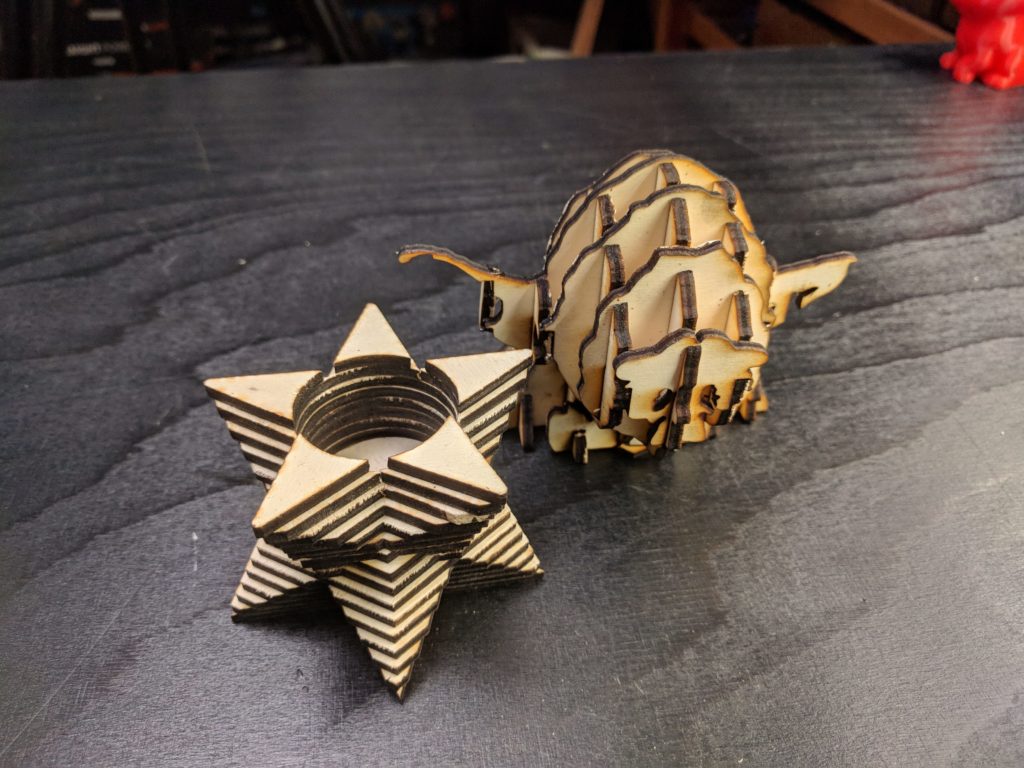
H3: Applications of Laser Cutting
- 3d Laser Engraving Machine 3D Laser Engraving Machine: Unlocking Precision And Versatility In Manufacturing
- 3d Christmas Ornaments Laser Cut 3D Christmas Ornaments Laser Cut: Elevate Your Holiday Decor With Precision And Creativity
- 3d Laser Cut Butterfly Framed Print 3D Laser Cut Butterfly Framed Print: An Exquisite Wall Art Masterpiece
- 3d Puzzle Laser Cut Files 3D Puzzle Laser Cut Files: A Comprehensive Guide For Designers And Makers
- 3d Laser Cutting Services 3D Laser Cutting Services: Precision And Innovation In Fabrication
- Precision: Laser cutting provides highly precise cuts with tolerances down to 0.001 inches.
- Automotive and aerospace components
- Medical devices and implants
- Electronic circuit boards
- Jewelry and accessories
- Home appliances and furniture
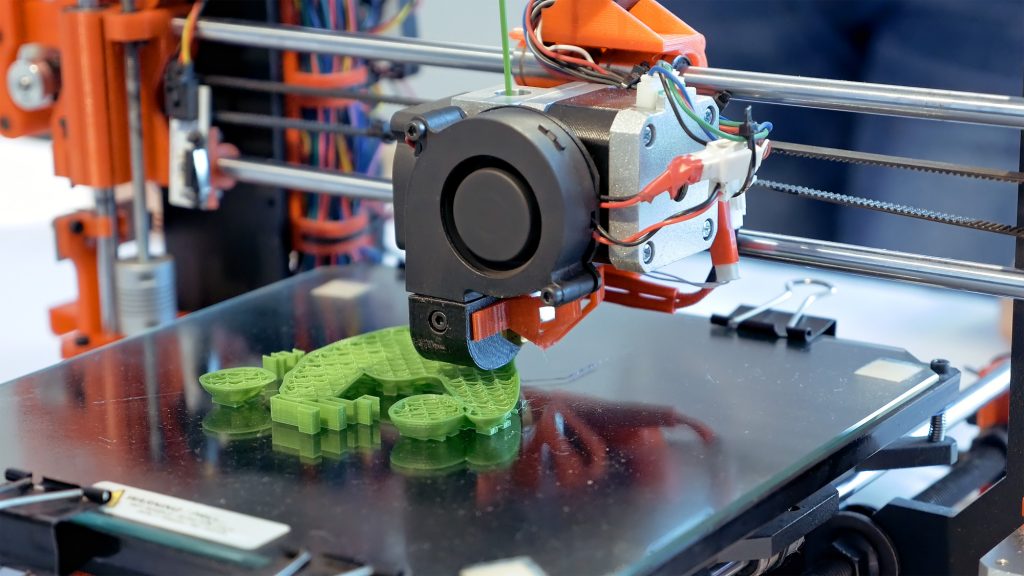
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing allows for quick and affordable creation of prototypes, reducing product development time.
- Customization: 3D printing enables the production of customized parts and products, tailored to specific needs.
- Complex Geometries: 3D printing can create complex shapes and geometries that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Reduced Material Waste: 3D printing only uses the material required for the part, minimizing waste.
- Increased Design Freedom: 3D printing allows designers to explore new design possibilities without the limitations of traditional manufacturing.
- Architectural models and prototypes
- Medical implants and prosthetics
- Industrial components and tooling
- Consumer products and gadgets
- Art and design objects
- Both laser cutting and 3D printing utilize computer-controlled technology.
- Both technologies offer high precision and accuracy.
- Both processes can be automated for high-volume production.
- Material Removal vs. Material Deposition: Laser cutting removes material to create a shape, while 3D printing adds material to build an object.
- Subtractive vs. Additive: Laser cutting is a subtractive process, removing material from a workpiece. 3D printing is an additive process, building up layers of material.
- Production Volume: Laser cutting is typically used for high-volume production, while 3D printing is better suited for prototyping and small-batch production.
- Material Range: Laser cutting can process a wider range of materials than 3D printing.
- Cost: Laser cutting is generally more cost-effective for high-volume production, while 3D printing is more suitable for prototyping and customized parts.
Laser cutting and 3D printing are two revolutionary manufacturing technologies that have transformed the way products are designed, produced, and customized. These technologies offer unparalleled precision, flexibility, and speed, enabling the creation of complex and intricate parts, prototypes, and finished goods.
Laser Cutting
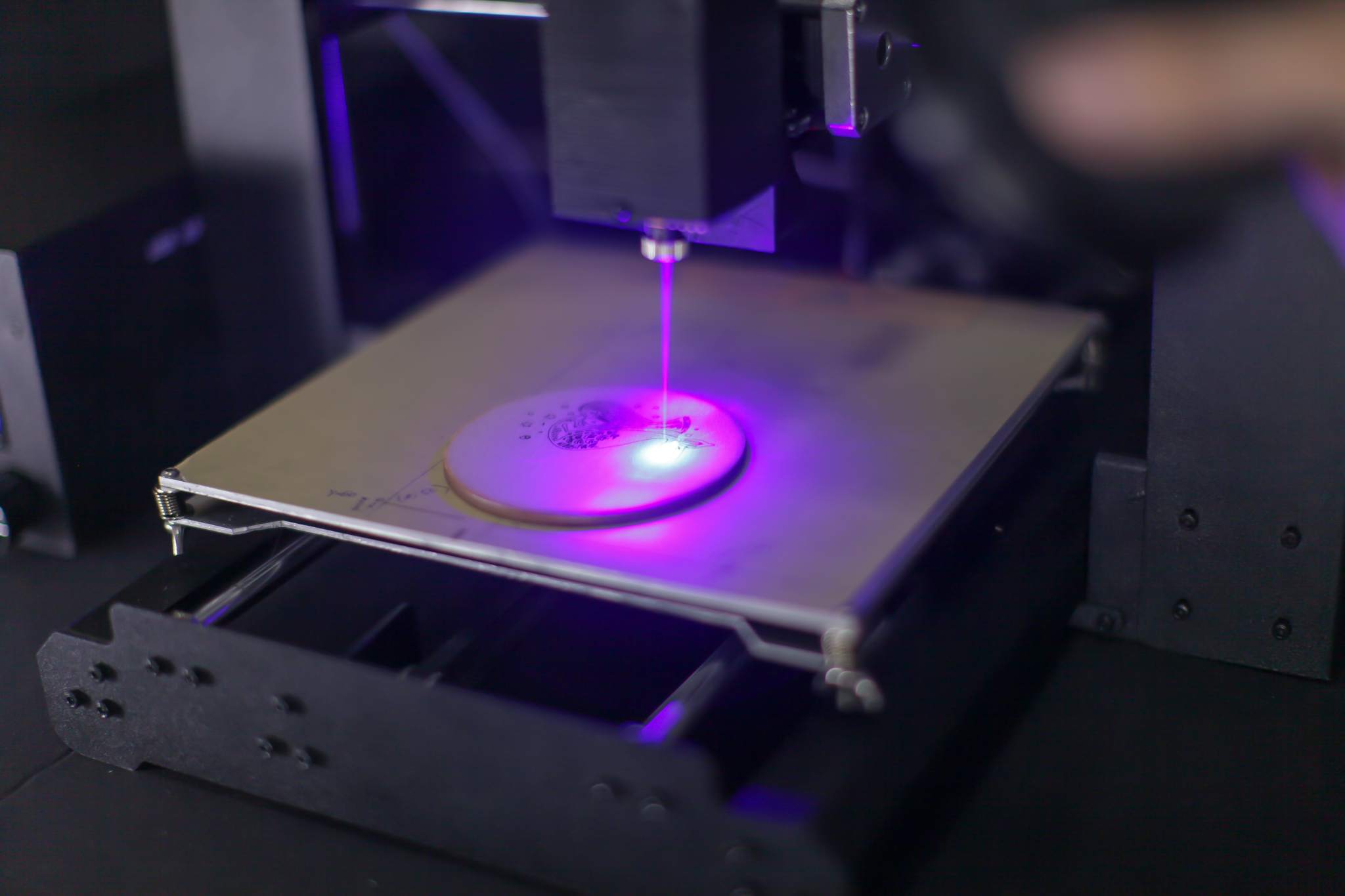
Laser cutting is a process that utilizes a highly focused laser beam to cut various materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites. The laser beam melts, vaporizes, or burns the material, creating precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones.
H2: Advantages of Laser Cutting
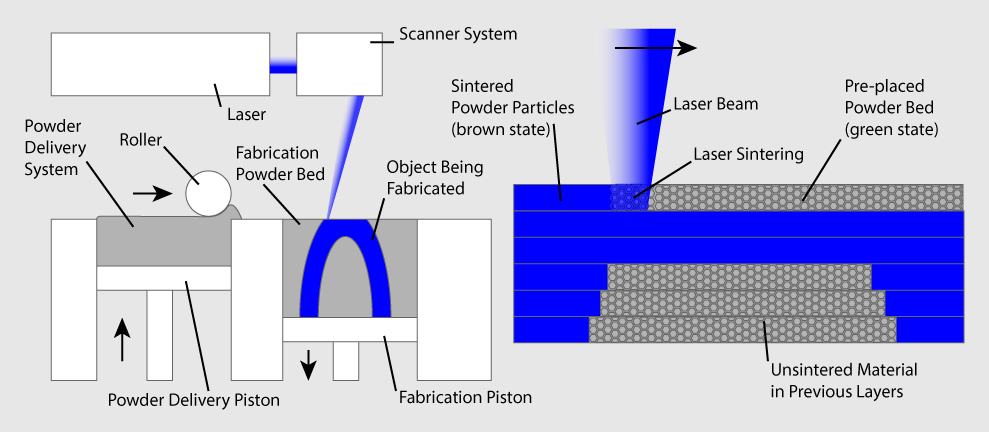
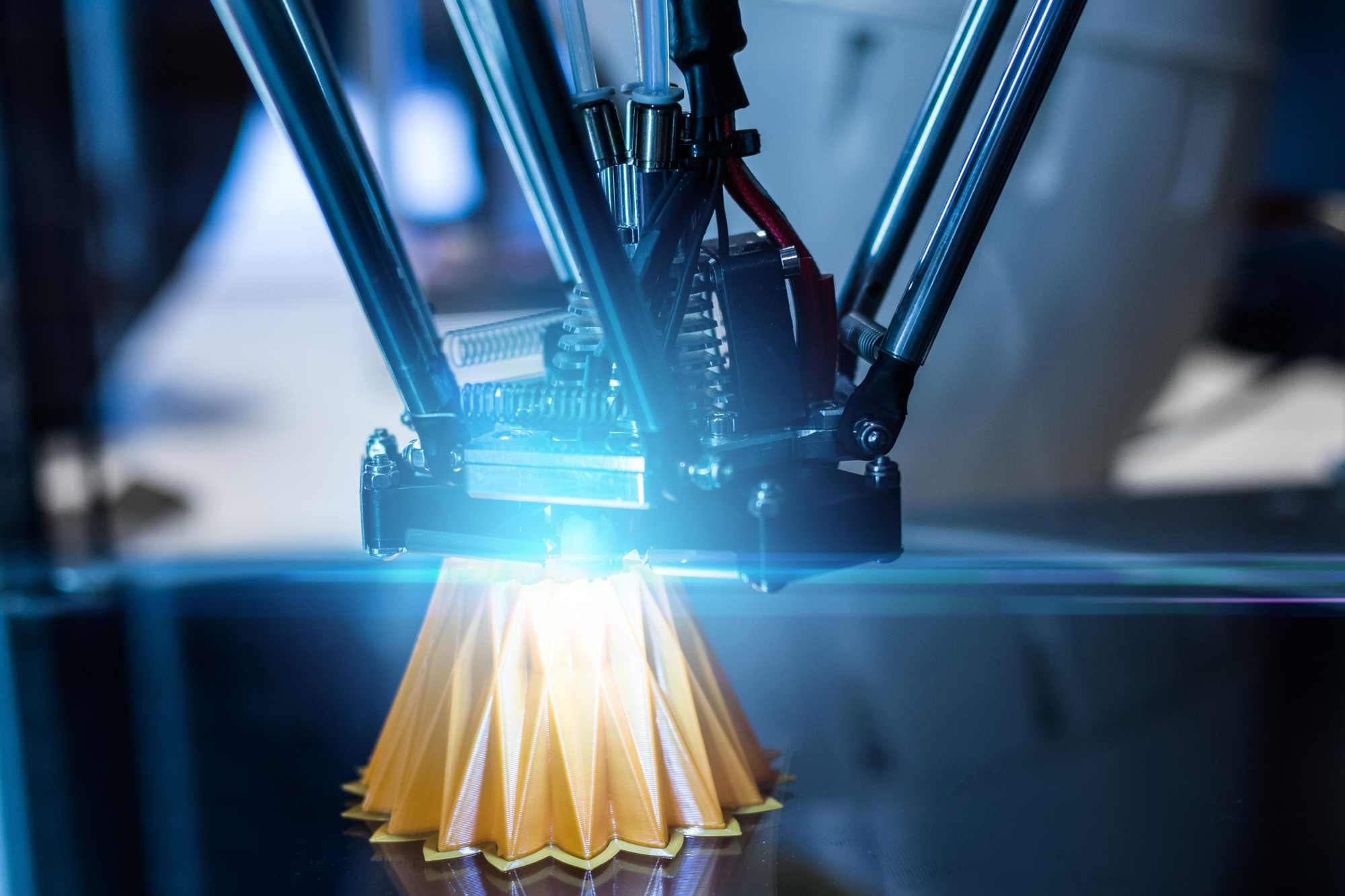
3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that builds three-dimensional objects from digital models. The printer deposits material layer by layer, gradually forming the desired shape.
H2: Advantages of 3D Printing
H3: Applications of 3D Printing
Laser Cutting vs. 3D Printing: A Comparative Analysis
H2: Similarities
H2: Differences
Conclusion
Laser cutting and 3D printing are two essential technologies that have revolutionized manufacturing. Laser cutting provides precision, speed, and versatility for cutting various materials. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, customization, and the creation of complex geometries. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each technology is crucial for choosing the optimal solution for specific manufacturing needs.
FAQs
Q: Which technology is better for prototyping?
A: 3D printing is ideal for rapid prototyping due to its ability to quickly create physical models from digital designs.
Q: Which technology is more suitable for high-volume production?
A: Laser cutting is typically more cost-effective for high-volume production, offering high speed and precision.
Q: Can laser cutting and 3D printing be used together?
A: Yes, laser cutting can be used to create intricate features or cut out parts printed using 3D printing.
Q: What are the potential applications of laser cutting and 3D printing in the future?
A: Future applications include advanced medical devices, personalized products, and innovative construction techniques.