What is 3D Laser Cutting?
Definition
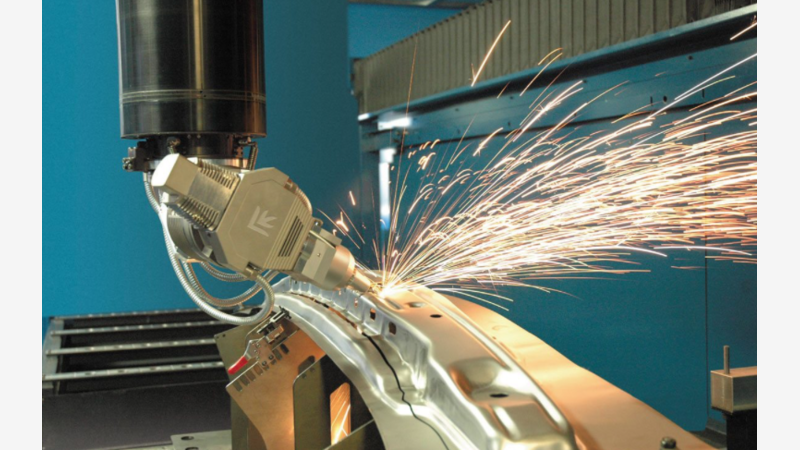
3D laser cutting is a cutting-edge technology that uses a laser to cut three-dimensional shapes from a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. Unlike traditional 2D laser cutting, which cuts flat sheets, 3D laser cutting allows for the creation of intricate, curved, and complex geometries.
Table of Content
- 1 What is 3D Laser Cutting?
- 1.1 Definition
- 1.2 Process
- 1.3 Advantages of 3D Laser Cutting
- 1.4 Process
- 1.5 Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
- 2 How Does 3D Laser Cutting Work?
- 2.6 Laser Sources
- 2.7 Beam Manipulation
- 2.8 Material Interaction
- 2.9 Cutting Path
- 3 Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
- 4 Factors Affecting 3D Laser Cutting Quality
- 5 Conclusion
- 6 FAQs
Process
- CAD Design: The desired 3D shape is designed using a computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Laser Beam Generation: A high-powered laser beam is generated by a laser source, typically a fiber laser or CO2 laser.
- Beam Manipulation: The laser beam is manipulated using mirrors, lenses, and beam expanders to achieve the desired focus and power distribution.
- Material Interaction: The laser beam is focused onto the material, causing it to melt, vaporize, or sublimate.
- Cutting Path: The laser beam follows a predefined path, cutting the material along the desired shape.
- Material Removal: The molten or vaporized material is removed from the cutting zone using an assist gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen.
Advantages of 3D Laser Cutting
- 3d Laser Cut Plane 3D Laser Cut Plane: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Crystal Laser Cutting Machine 3D Crystal Laser Cutting Machine: A Comprehensive Guide
- Dxf 3d Laser Cut H1: Unleashing The Power Of DXF 3D Laser Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3d Laser Cut Tree 3D Laser Cut Tree: A Revolutionary Home Décor Element
- 3d Laser Cut Ideas 3D Laser Cut Ideas: Unleashing Creativity And Precision
- CAD Design: The desired 3D shape is designed using a computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Laser Beam Generation: A high-powered laser beam is generated by a laser source, typically a fiber laser or CO2 laser.
- Precision and Accuracy: 3D laser cutting provides high precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of complex shapes with tight tolerances.
- Versatility: It can cut a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, making it suitable for various applications.
- Speed and Efficiency: 3D laser cutting is a fast and efficient process, significantly reducing production times compared to traditional methods.
- Reduced Waste: The laser cutting process minimizes material waste, as the beam follows a precise path and only removes the necessary material.
- Customization: 3D laser cutting enables the production of customized and personalized products with unique designs.
3D laser cutting is a cutting-edge technology that uses a laser to cut three-dimensional shapes from a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. Unlike traditional 2D laser cutting, which cuts flat sheets, 3D laser cutting allows for the creation of intricate, curved, and complex geometries.
Process
The process of 3D laser cutting involves the following steps:
Applications of 3D Laser Cutting
- Aerospace: Cutting precision parts for aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft.
- Automotive: Manufacturing custom components, exhaust systems, and interior trim.
- Medical: Creating medical devices, implants, and surgical instruments.
- Consumer Products: Producing toys, electronics, and home appliances with intricate designs.
- Architecture: Cutting architectural panels, facades, and decorative elements.
How Does 3D Laser Cutting Work?
Laser Sources
The most common laser sources used in 3D laser cutting are:
- Fiber Lasers: Compact and efficient, providing high power and beam quality.
- CO2 Lasers: Powerful and versatile, suitable for cutting a wide range of materials.
Beam Manipulation
The laser beam is manipulated using various optical components:
- Mirrors: Direct and steer the beam along the desired path.
- Lenses: Focus the beam to achieve the required power density.
- Beam Expanders: Increase the beam diameter to improve cutting speed and reduce heat-affected zones.
Material Interaction
The laser beam interacts with the material in one of three ways:
- Melting: The laser beam melts the material, and the molten material is removed by an assist gas.
- Vaporization: The laser beam vaporizes the material, creating a clean and precise cut.
- Sublimation: The laser beam directly converts the material from solid to gas, leaving no residue.
Cutting Path
The cutting path is determined by the CAD design and is controlled by a computer numerical control (CNC) system. The CNC system guides the laser beam along the desired trajectory, ensuring precision and accuracy.
Materials Suitable for 3D Laser Cutting
- Metals: Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and other alloys
- Plastics: Acrylic, polycarbonate, ABS, and other thermoplastics
- Wood: Plywood, MDF, hardwoods, and softwoods
- Ceramics: Tiles, glass, and other ceramic materials
- Composites: Carbon fiber, fiberglass, and other reinforced materials
Factors Affecting 3D Laser Cutting Quality
- Laser Power: Higher power lasers provide faster cutting speeds and deeper cuts.
- Beam Quality: A high beam quality produces a more focused beam, resulting in cleaner and more precise cuts.
- Cutting Speed: The cutting speed determines the width and depth of the cut.
- Assist Gas: The assist gas protects the cutting zone from oxidation and helps remove molten material.
- Material Properties: The type of material and its thickness influence the laser cutting parameters.
Conclusion
3D laser cutting is a transformative technology that revolutionizes manufacturing processes. Its precision, versatility, speed, and customization capabilities make it an ideal solution for creating complex and intricate shapes from a wide range of materials. As the technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play an increasingly significant role in various industries, from aerospace to medical and consumer products.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between 3D laser cutting and 2D laser cutting?
A: 3D laser cutting cuts three-dimensional shapes, while 2D laser cutting cuts flat sheets.
Q: What is the maximum thickness that can be cut with 3D laser cutting?
A: The maximum thickness depends on the material and the laser power. Typically, metals up to 25mm thick can be cut, while plastics and wood can be cut up to 100mm thick.
Q: What are the safety precautions for 3D laser cutting?
A: Safety precautions include wearing protective eyewear, using proper ventilation, and adhering to laser safety protocols.
Q: Is 3D laser cutting suitable for small-scale production?
A: Yes, 3D laser cutting is suitable for both small-scale and large-scale production. Its versatility and speed make it an efficient option for creating customized and one-off products.
Q: What is the future of 3D laser cutting?
A: The future of 3D laser cutting is promising, with advancements in laser technology, automation, and materials science expected to further enhance its capabilities and applications.